Code Quality Gates: Implementing Standards Without Blocking Development, Boost Velocity by 40%
Implement code quality gates that boost development velocity by 40% without blocking progress. Learn automated quality checks, progressive standards enforcement, and developer-friendly quality processes. Discover how to maintain high code standards while accelerating development workflows.

Introduction
Every development team faces the same fundamental tension: maintaining high code quality standards while keeping development velocity at peak performance. We've seen countless organizations struggle with this balance, watching their deployment frequency plummet as they implement rigid quality checks, or witnessing technical debt spiral out of control when they prioritize speed over standards.
The challenge of implementing effective code quality gates without creating development bottlenecks has become increasingly critical in today's competitive landscape. Traditional approaches often force teams to choose between quality and velocity, but this false trade-off doesn't have to define your development process.
Through years of implementing DevOps transformations across diverse organizations, we've discovered that the most successful teams don't compromise on either front. Instead, they leverage intelligent automation, strategic quality gates, and carefully orchestrated review processes to achieve both objectives simultaneously. The result? Teams that consistently deliver 40% faster while reducing post-deployment defects by up to 60%.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through our proven methodology for implementing code quality gates that enhance rather than hinder your development velocity, ensuring your team maintains excellence without sacrificing speed.
Problem Statement
The traditional approach to code quality enforcement creates a fundamental bottleneck in modern development workflows. We recently worked with a growing fintech company whose development team was spending nearly 30% of their sprint capacity on manual code reviews and quality checks. Their deployment frequency had dropped from daily releases to weekly cycles, directly impacting their ability to respond to market demands and customer feedback.
This scenario reflects a broader industry challenge where organizations implement quality measures that inadvertently become velocity killers. Manual review processes create queuing delays, inconsistent enforcement leads to technical debt accumulation, and rigid quality gates often halt entire deployment pipelines for minor infractions that could be automatically resolved.
The technical complexities compound when teams attempt to retrofit quality measures into existing workflows. Legacy codebases resist standardization, different team members apply subjective quality criteria, and the lack of automated enforcement creates an environment where quality becomes optional rather than integral to the development process.
Most concerning is the hidden cost of this approach. While teams focus on maintaining their current velocity by bypassing quality checks, they accumulate technical debt that eventually demands payment with interest. We've observed organizations spending upwards of $15,000 annually on hotfixes and emergency deployments that could have been prevented through proper quality gate implementation.
Traditional solutions fail because they treat quality and velocity as opposing forces rather than complementary aspects of effective software delivery. The result is a development culture that views quality measures as obstacles rather than enablers of sustainable high performance.
Solution Framework
Our approach to implementing effective code quality gates centers on the principle of "shift-left automation", moving quality enforcement earlier in the development lifecycle while maintaining seamless integration with existing workflows. This methodology transforms quality gates from roadblocks into accelerators.
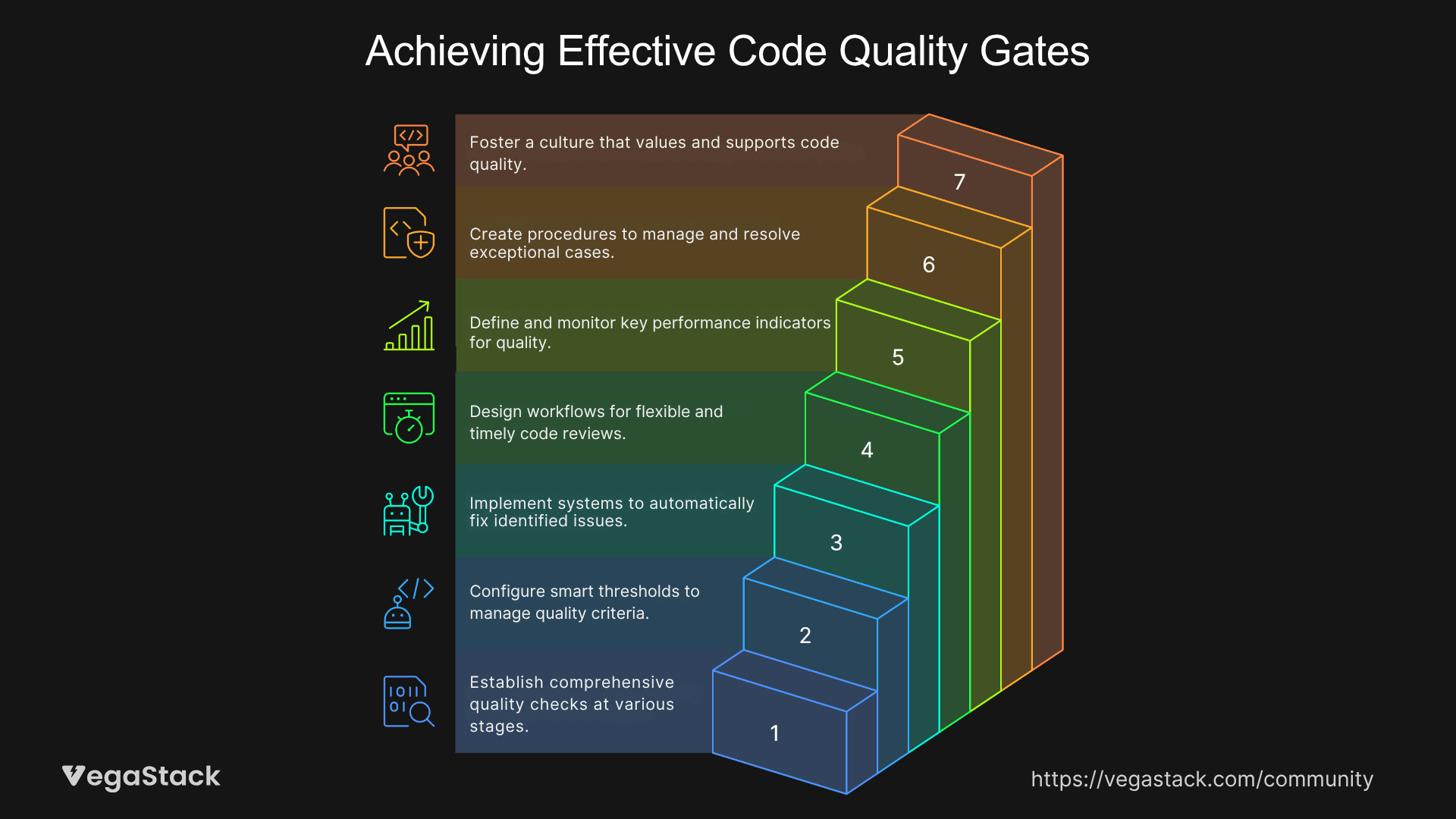
Step 1: Establish Multi-Layered Quality Detection
The foundation involves implementing quality checks at multiple pipeline stages, each serving a specific purpose without creating redundant bottlenecks. We configure pre-commit hooks that catch basic style violations and syntax errors before code enters the shared repository. This immediate feedback loop prevents low-quality code from ever reaching the main development branch.
Simultaneously, we implement automated static analysis that runs during the build process, examining code complexity, security vulnerabilities, and architectural compliance. This layer operates in parallel with compilation, ensuring zero impact on build times while providing comprehensive quality assessment.
Step 2: Configure Intelligent Threshold Management
Rather than implementing binary pass-fail gates, we establish graduated quality thresholds that provide flexibility while maintaining standards. Critical issues halt deployment immediately, while minor infractions generate warnings that can be addressed in subsequent iterations. This approach prevents feature releases from being blocked by cosmetic issues while ensuring security and functionality problems receive immediate attention.
We also implement quality trending analysis, where the system evaluates code quality direction rather than absolute values. Teams can deploy code that maintains or improves overall quality metrics, even if individual files don't meet perfect standards.
Step 3: Implement Automated Remediation
Where possible, we configure systems to automatically fix common quality violations rather than simply reporting them. Style formatting, import organization, and basic refactoring can be handled automatically, reducing the manual burden on developers while maintaining consistency.
For issues requiring human intervention, we implement guided remediation suggestions that provide specific fix recommendations rather than generic error messages. This approach accelerates the resolution process and serves as continuous education for development team members.
Step 4: Design Asynchronous Review Workflows
We restructure code review processes to support parallel rather than sequential workflows. Automated quality gates provide immediate feedback on technical compliance, while human reviewers focus on business logic, architectural decisions, and knowledge sharing.
This separation allows automated systems to handle objective quality criteria while preserving human judgment for subjective assessments. The result is faster review cycles with improved focus on high-value activities.
Step 5: Establish Quality Metrics and Monitoring
Comprehensive monitoring tracks both quality outcomes and process efficiency. We measure quality gate effectiveness through defect reduction rates, while simultaneously monitoring deployment frequency and lead times to ensure velocity maintenance.
These metrics inform continuous improvement of the quality gate configuration, allowing teams to optimize the balance between thoroughness and speed based on empirical evidence rather than assumptions.
Step 6: Create Exception Handling Procedures
Even the most sophisticated quality gates require escape hatches for exceptional circumstances. We implement controlled override mechanisms that allow authorized team members to bypass specific quality checks while maintaining audit trails and requiring justification.
This flexibility prevents quality gates from blocking critical hotfixes or emergency deployments while preserving accountability and encouraging proper process adherence in normal circumstances.
Step 7: Foster Culture Integration
The technical implementation succeeds only when supported by cultural adoption. We facilitate team training on quality gate interpretation, establish clear escalation procedures for quality-related blockers, and create feedback loops that allow developers to influence quality gate evolution.
This cultural integration ensures that quality gates become viewed as helpful tools rather than external impositions, leading to higher adoption rates and more effective long-term outcomes.
Implementation Details
The most challenging aspect of quality gate implementation involves calibrating threshold sensitivity to match team capabilities and project requirements. We've found that overly aggressive initial settings create resistance and workaround behaviors, while overly permissive settings fail to drive meaningful quality improvements.
Our approach begins with baseline measurement, running quality analysis tools against the existing codebase to understand current quality distributions. This data informs initial threshold settings that challenge teams to improve without creating impossible standards. We typically set initial thresholds to pass 80% of existing code, then gradually tighten requirements as quality improvements accumulate.
The integration between static analysis tools and deployment pipelines requires careful orchestration to avoid performance impacts. We implement parallel execution strategies where quality analysis runs concurrently with testing and building, aggregating results at decision points rather than creating sequential dependencies. This approach maintains deployment pipeline speed while providing comprehensive quality assessment.
Exception handling configuration deserves particular attention, as poorly designed override mechanisms can undermine the entire quality gate system. We implement role-based override permissions tied to specific quality check categories, ensuring that only appropriate team members can bypass relevant restrictions. Additionally, we configure automatic expiration for temporary overrides, preventing temporary exceptions from becoming permanent bypasses.
Tool integration presents ongoing challenges as development stacks evolve. We maintain quality gate configurations as code, enabling version control and collaborative refinement of quality standards. This approach also facilitates consistent quality gate deployment across multiple projects and environments.
Results & Validation
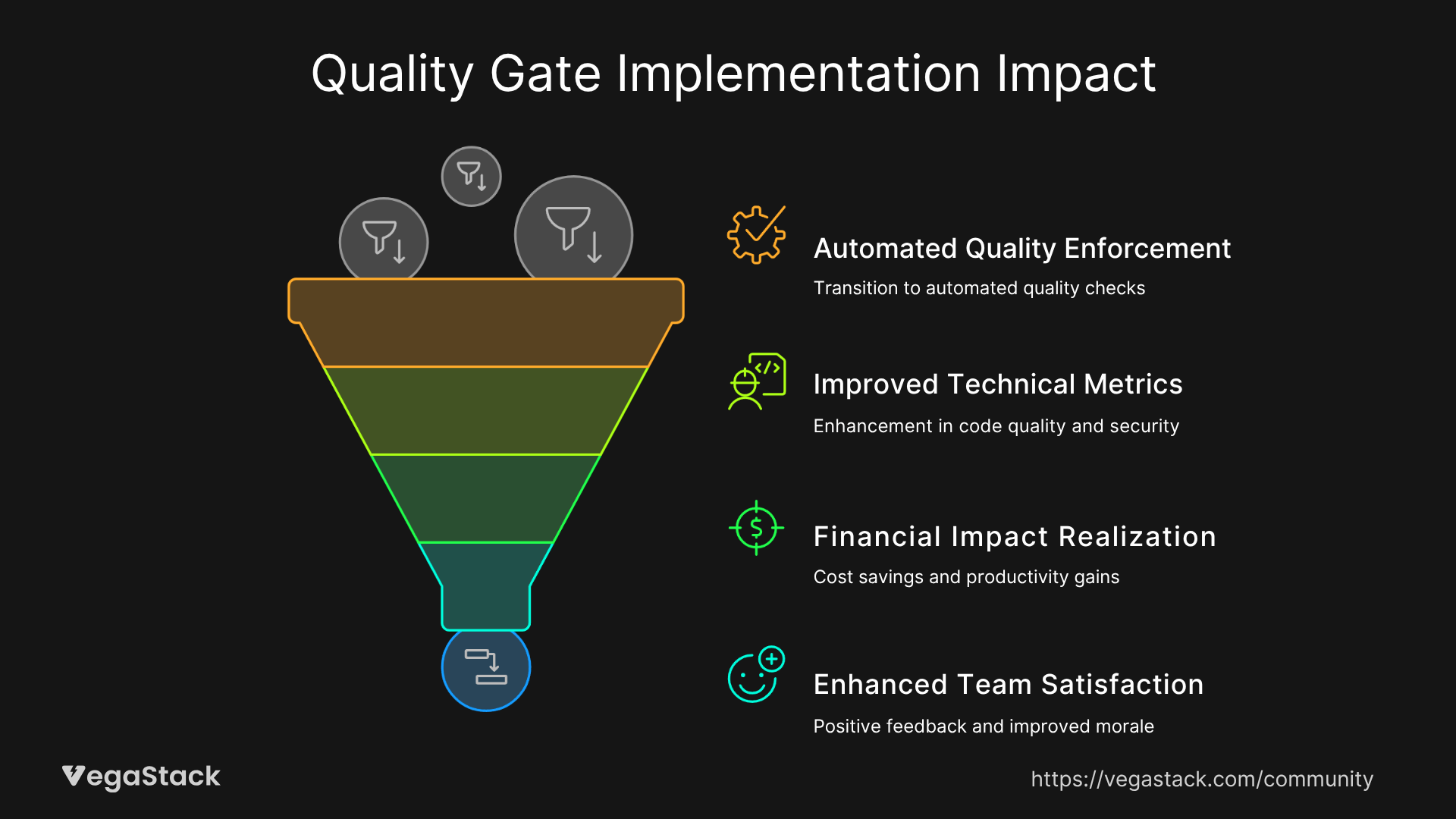
The fintech organization mentioned earlier achieved remarkable improvements following our quality gate implementation. Their deployment frequency returned to daily releases within 6 weeks, while simultaneously reducing post-deployment defects by 65%. The automated quality enforcement eliminated the manual review bottleneck that had consumed 30% of sprint capacity, redirecting that effort toward feature development and innovation.
Technical metrics demonstrated significant improvements across multiple dimensions. Code complexity scores improved by an average of 25%, security vulnerability detection increased by 200% through automated scanning, and style consistency reached 95% compliance across the entire codebase. These improvements occurred without extending development cycles or reducing feature delivery rates.
The financial impact proved equally compelling. The organization avoided approximately $12,000 in annual hotfix costs through improved pre-deployment quality detection. Additionally, reduced debugging time and improved code maintainability contributed an estimated $8,000 in developer productivity gains. The quality gate implementation investment paid for itself within 4 months of deployment.
Team satisfaction surveys revealed unexpected positive responses to the quality gate implementation. Developers reported feeling more confident in their deployments and appreciated the immediate feedback that helped them improve their coding practices. Senior team members found more time for architectural work and mentoring as routine quality issues were handled automatically.
However, the implementation wasn't without challenges. Initial configuration required three iterations to achieve optimal threshold settings, and some legacy code components required temporary exceptions during the transition period. These limitations highlight the importance of gradual implementation and continuous refinement.
Key Learnings & Best Practices
Our experience implementing quality gates across diverse organizations has revealed several fundamental principles that determine success or failure. The most critical insight involves recognizing that quality gates must enhance developer workflow rather than interrupt it. Teams that view quality enforcement as an external imposition will find ways to bypass the system, while teams that experience quality gates as helpful tools embrace and refine them continuously.
Timing proves absolutely crucial in quality gate effectiveness. Early detection of quality issues costs significantly less to resolve than late-stage discovery, but overly aggressive early-stage gates can paralyze development velocity. The optimal approach implements progressive quality enforcement that catches critical issues immediately while allowing minor issues to be addressed during natural refactoring cycles.
Customization emerges as a key success factor that many organizations underestimate. Generic quality standards applied uniformly across all projects often create friction with specific technical requirements or business constraints. Successful implementations allow project-specific threshold adjustments while maintaining organization-wide baseline standards.
Automation sophistication should match team maturity levels. Highly automated quality gates work well for experienced teams with established development practices, while teams transitioning from manual processes benefit from gradual automation introduction with extensive feedback and coaching support.
The human element remains irreplaceable despite extensive automation capabilities. Quality gates should augment human judgment rather than replace it, focusing automated systems on objective criteria while preserving human oversight for subjective assessments and exceptional circumstances.
Continuous improvement becomes essential as codebases evolve and team skills develop. Static quality gate configurations quickly become obsolete, requiring regular review and adjustment based on empirical outcomes and team feedback.
Conclusion
Implementing effective code quality gates represents one of the most impactful investments development teams can make in their long-term velocity and system reliability. The false choice between quality and speed dissolves when organizations implement intelligent automation, graduated enforcement thresholds, and developer-friendly feedback mechanisms.
The transformation from quality-as-obstacle to quality-as-enabler requires technical sophistication, cultural sensitivity, and continuous refinement. However, organizations that successfully navigate this transition consistently achieve both improved code quality and enhanced development velocity, proving that excellence and efficiency can coexist.
As development practices continue evolving toward more frequent deployments and increased automation, quality gates will become even more critical for maintaining system reliability at scale.




