Container Performance Optimization: Right-Sizing for Maximum Efficiency and 40% Cost Reduction
Maximize container efficiency and cut costs by 40% with strategic optimization and right-sizing. Learn resource allocation, performance tuning, and cost-saving techniques to boost container performance while reducing infrastructure expenses.
Introduction
We've all been there - staring at a cloud bill that's significantly higher than expected, wondering where all those compute resources went. In our experience working with containerized applications, we've discovered that one of the most impactful yet overlooked aspects of container performance optimization is proper right-sizing. The reality is that most organizations either massively over-provision their containers out of fear of performance issues or under-provision them, leading to application instability.
Container right-sizing isn't just about cutting costs; it's about finding that sweet spot where your applications perform optimally while consuming exactly the resources they need. Through systematic profiling techniques and strategic monitoring approaches, we've helped teams achieve remarkable results - typically seeing 25-40% reduction in infrastructure costs while simultaneously improving application performance and reliability.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through our proven methodology for container resource optimization, sharing the techniques we've refined through years of production deployments. Whether you're managing a handful of microservices or orchestrating hundreds of containers, these strategies will transform how you approach resource allocation and performance tuning.
The Hidden Cost of Container Resource Misallocation
The challenge with container resource allocation runs deeper than most teams realize. We recently worked with a mid-sized e-commerce company running their platform on Kubernetes, where they were spending approximately $8,000 monthly on their container infrastructure. Their development team, following the "better safe than sorry" principle, had configured their containers with generous resource limits, typically 2-4 times what their applications actually required during normal operations.
The problem manifested in multiple ways: nodes were consistently running at low utilization rates, scaling decisions were based on inaccurate resource assumptions, and the finance team was questioning the ROI of their cloud-native transformation. Traditional monitoring approaches were failing because they focused on infrastructure metrics rather than application-specific resource consumption patterns.
What made this particularly challenging was the dynamic nature of containerized workloads. Unlike traditional virtual machines where you might set resource allocation once and forget about it, containers in modern orchestration platforms face constantly changing demands. Peak traffic periods, batch processing jobs, and varying user loads create a complex resource consumption landscape that static allocation simply cannot handle effectively.
The technical complexity increases when you consider that different types of applications have vastly different resource profiles. CPU-intensive services like image processing workloads have different optimization requirements compared to memory-heavy applications like in-memory databases or I/O-intensive services handling file uploads.
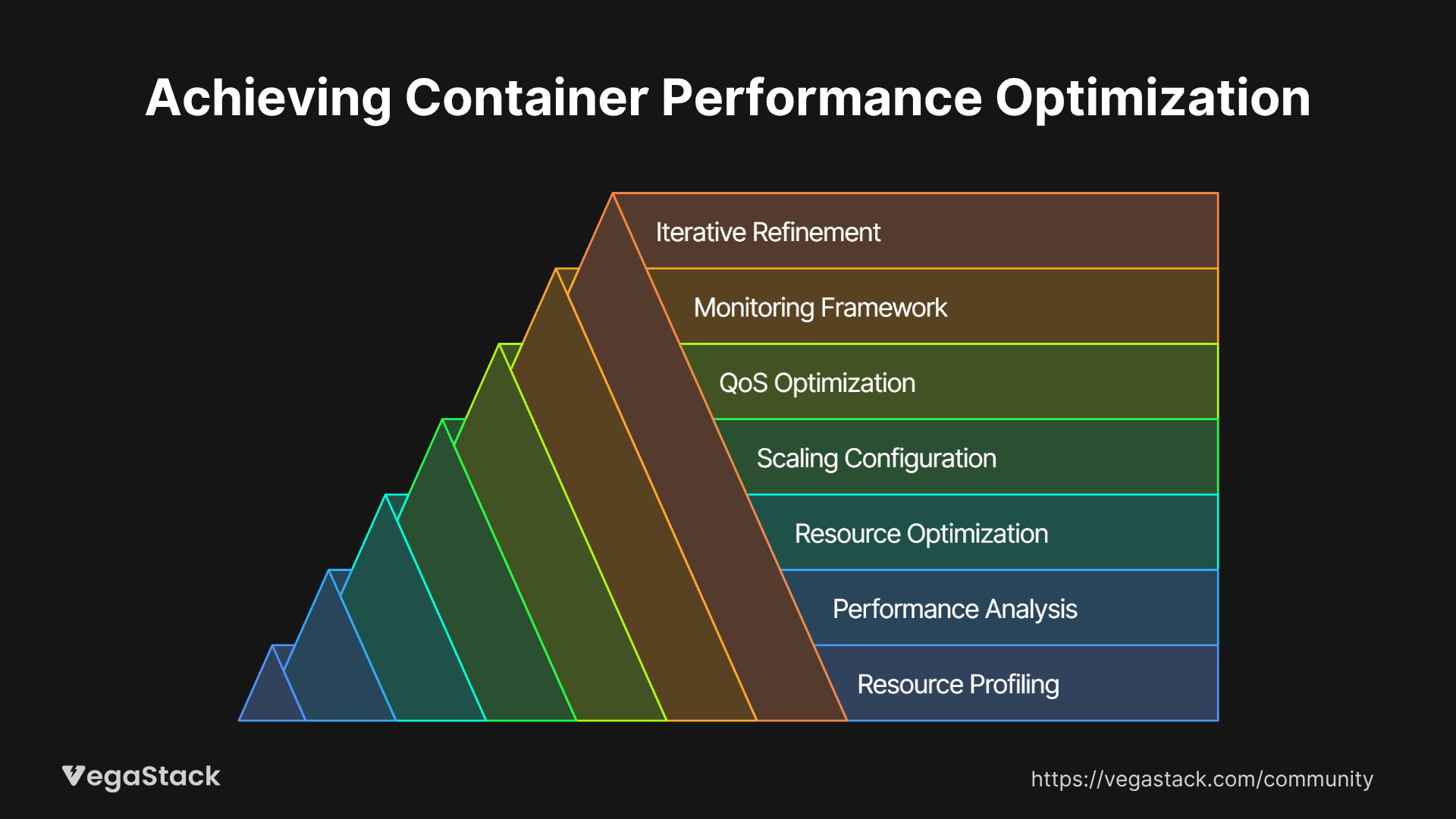
Our Systematic Container Right-Sizing Framework
Through extensive testing and real-world implementations, we've developed a 7-step framework for container performance optimization that addresses both immediate cost concerns and long-term scalability requirements.
Step 1: Comprehensive Resource Profiling and Baseline Establishment
The foundation of effective right-sizing begins with understanding your current resource consumption patterns. We start by implementing detailed monitoring across three critical dimensions: CPU utilization patterns, memory consumption trends, and I/O characteristics. This isn't just about collecting metrics; it's about understanding the story your applications tell through their resource usage.
During this phase, we establish baseline measurements across different operational scenarios - normal business hours, peak traffic periods, batch processing windows, and maintenance cycles. The key insight we've learned is that you need at least 2 weeks of continuous monitoring to capture meaningful patterns, including weekend variations and monthly business cycles.
Step 2: Application-Specific Performance Characteristics Analysis
Every application has unique performance fingerprints, and recognizing these patterns is crucial for effective optimization. We categorize applications into performance archetypes: steady-state services that maintain consistent resource consumption, burst-pattern applications that experience predictable spikes, and variable-load services with unpredictable resource demands.
This classification drives our optimization strategy because each archetype requires different approaches to resource allocation and scaling parameters. Steady-state services benefit from tight resource limits with minimal overhead, while burst-pattern applications need carefully configured resource requests with higher limits to accommodate spikes.
Step 3: Resource Request and Limit Optimization Strategy
The relationship between resource requests and limits forms the core of container right-sizing. We've found that the traditional approach of setting conservative requests and high limits often leads to resource waste and scheduling inefficiencies. Instead, we implement a graduated approach where resource requests closely match observed baseline consumption, while limits are set based on acceptable performance degradation thresholds.
Our methodology involves calculating optimal resource requests at the 75th percentile of observed usage, ensuring that containers receive adequate resources for normal operations while allowing the orchestration platform to make efficient scheduling decisions. For limits, we typically set them at the 95th percentile, providing headroom for legitimate spikes while preventing resource hoarding.
Step 4: Horizontal and Vertical Scaling Configuration
Right-sizing isn't just about individual container resources; it's about optimizing the entire scaling strategy. We implement horizontal pod autoscaling with carefully tuned metrics that reflect actual application performance rather than simple CPU thresholds. This often involves custom metrics based on application-specific indicators like queue depths, response times, or business transaction volumes.
Vertical scaling considerations become particularly important for stateful applications where horizontal scaling isn't always feasible. We configure vertical pod autoscaling with gradual resource adjustments that prevent the feast-or-famine cycle of dramatic resource changes.
Step 5: Quality of Service Class Optimization
Kubernetes Quality of Service classes significantly impact both performance and cost efficiency. We strategically assign QoS classes based on application criticality and resource predictability. Critical services typically receive Guaranteed QoS class with tightly matched requests and limits, while development workloads might use BestEffort class for maximum cost efficiency.
The subtle but important consideration here is understanding how QoS class assignment affects node utilization and scheduling efficiency. We've observed that a thoughtful mix of QoS classes across your cluster can improve overall resource utilization by 15-25%.
Step 6: Continuous Monitoring and Alerting Framework
Effective right-sizing requires ongoing vigilance through comprehensive monitoring strategies. We implement multi-layered alerting that captures both immediate performance issues and gradual resource consumption trends. This includes threshold-based alerts for resource exhaustion, trend analysis for capacity planning, and efficiency metrics that track the success of optimization efforts.
The monitoring framework extends beyond basic resource metrics to include application performance indicators, user experience metrics, and cost efficiency measurements. This holistic approach ensures that optimization efforts don't inadvertently impact application quality.
Step 7: Iterative Refinement and Validation Process
Container right-sizing isn't a one-time activity; it's an ongoing process of refinement and optimization. We establish regular review cycles where resource allocations are evaluated against actual performance data and adjusted based on changing application requirements or usage patterns.
Implementation: Profiling Techniques and Tools
The most challenging aspect of container right-sizing often lies in accurate profiling and data collection. Traditional monitoring approaches frequently miss the nuanced resource consumption patterns that are critical for optimization decisions. We've developed a multi-faceted profiling strategy that captures both quantitative metrics and qualitative performance characteristics.
Resource profiling begins with establishing comprehensive observability across your container infrastructure. This involves implementing monitoring agents that capture detailed CPU, memory, network, and storage metrics at both the container and application levels. The key insight we've learned is that you need monitoring granularity that matches your optimization goals - if you're optimizing for cost efficiency, you need cost-relevant metrics; if you're optimizing for performance, you need performance-specific indicators.
Memory profiling requires particular attention because memory usage patterns in containerized applications can be deceptive. We implement monitoring that distinguishes between different types of memory usage: heap memory for application data, buffer memory for I/O operations, and cached memory that can be reclaimed under pressure. This granular understanding prevents the common mistake of over-provisioning memory based on total usage rather than actual application requirements.
CPU profiling focuses on understanding both utilization patterns and performance characteristics. We monitor CPU usage across different time scales - second-by-second for burst detection, minute-by-minute for operational patterns, and hour-by-hour for capacity planning. The critical insight is that CPU optimization isn't just about average utilization; it's about understanding the relationship between CPU availability and application performance.
Network and storage I/O profiling often reveals optimization opportunities that pure CPU and memory analysis miss. Applications with high I/O requirements might benefit from different resource allocation strategies, and understanding these patterns helps inform both resource allocation and infrastructure architecture decisions.
Measuring Success: Performance Gains and Cost Optimization Results
The effectiveness of container right-sizing initiatives becomes apparent through both technical metrics and business outcomes. In our experience with the e-commerce company mentioned earlier, implementing our systematic optimization framework resulted in impressive improvements across multiple dimensions.
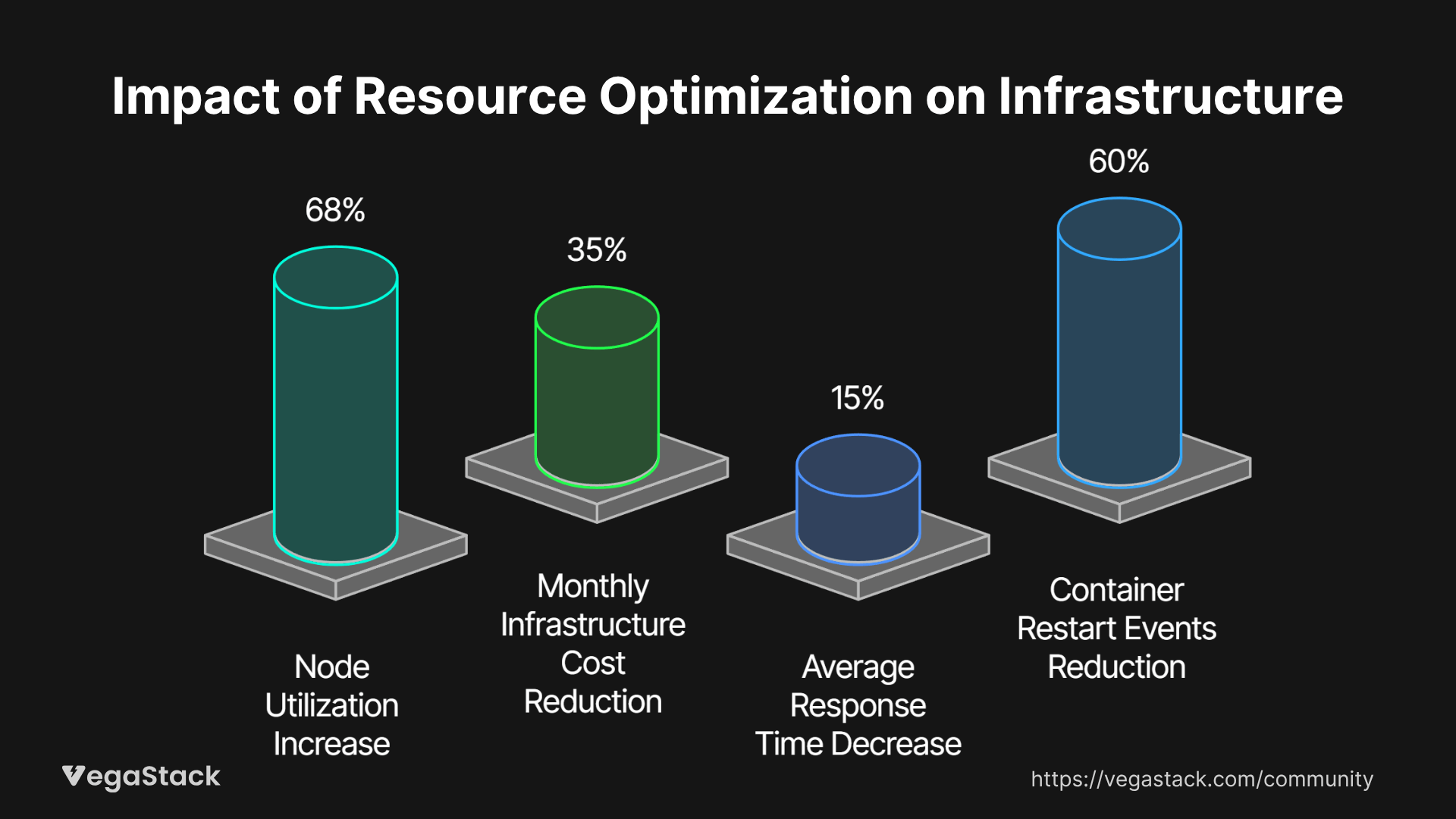
Resource utilization efficiency improved dramatically, with average node utilization increasing from 35% to 68% while maintaining application performance standards. This improvement translated directly into cost savings, reducing their monthly infrastructure spend from $8,000 to approximately $5,200 - a 35% reduction that freed up budget for other strategic initiatives.
Application performance metrics showed concurrent improvements, with average response times decreasing by 15% due to more efficient resource allocation and reduced resource contention. The most significant improvement came in application stability, with container restart events decreasing by 60% as right-sized containers experienced fewer resource-related failures.
Perhaps most importantly, the optimization efforts improved the predictability of infrastructure costs. Instead of experiencing unexpected bill spikes during traffic increases, the right-sized infrastructure scaled more predictably, making capacity planning and budget forecasting significantly more accurate.
The business impact extended beyond direct cost savings. Development teams reported increased confidence in their deployment processes, operations teams gained better visibility into application resource requirements, and the finance team could more accurately model the costs of new feature development.
Key Learnings and Container Optimization Best Practices
Through numerous right-sizing implementations, we've identified several fundamental principles that consistently drive successful outcomes. These insights go beyond specific technical configurations to address the broader strategic approach to container resource optimization.
Start with comprehensive observability before making optimization decisions: We've learned that premature optimization based on assumptions rather than data often leads to performance issues that are difficult to diagnose. Investing time in proper monitoring and profiling pays dividends throughout the optimization process.
Resource right-sizing is an iterative process, not a one-time configuration: Application resource requirements evolve with business growth, feature additions, and changing usage patterns. Successful optimization requires establishing processes for ongoing monitoring and adjustment rather than treating it as a project with a defined end point.
Consider the entire application ecosystem when optimizing individual containers: Resource optimization decisions for one service can impact the performance characteristics of dependent services. We've found that taking a holistic view of application architecture leads to better optimization outcomes than focusing solely on individual container metrics.
Balance cost optimization with performance reliability: While aggressive right-sizing can drive significant cost savings, pushing resource limits too tightly can impact application reliability and user experience. The most successful implementations find the optimal balance between efficiency and reliability based on business requirements.
Automate optimization processes wherever possible: Manual resource allocation quickly becomes unmanageable as container deployments scale. Implementing automated scaling policies, monitoring alerts, and optimization workflows ensures that right-sizing efforts remain effective as your infrastructure grows.
Document and share optimization knowledge across teams: Container right-sizing involves both technical understanding and business context. Creating documentation and training materials helps ensure that optimization knowledge spreads throughout your organization rather than remaining concentrated in a few individuals.
Conclusion
Container performance optimization through systematic right-sizing represents one of the most impactful strategies for improving both application performance and infrastructure efficiency. The methodology we've outlined provides a structured approach to understanding, optimizing, and maintaining container resource allocation that delivers measurable results.
The key to successful container right-sizing lies in combining comprehensive data collection with strategic analysis and continuous refinement. By implementing proper profiling techniques, establishing monitoring frameworks, and maintaining an iterative approach to optimization, organizations can achieve significant cost savings while improving application performance and reliability.
As containerized infrastructure continues to evolve, the organizations that master resource optimization will maintain competitive advantages through both cost efficiency and operational excellence. The question isn't whether you should optimize your container resources, but how quickly you can implement a systematic approach that delivers results.




