Deployment Automation: How Self-Service Release Capabilities Reduce Release Time by 75%
Accelerate your release process with deployment automation and self-service capabilities that reduce release time by 75%. Learn how to implement automated deployment pipelines, streamline release workflows, and empower teams with efficient, reliable deployment processes that scale with growth.
Introduction
Picture this scenario: It's 5 PM on a Friday, and your development team discovers a critical bug that needs immediate deployment. Instead of calling the operations team, creating emergency tickets, and waiting for manual approvals, your developers simply push their fix through an automated pipeline that handles everything from security scanning to production deployment. This isn't a DevOps fantasy - it's the reality of effective deployment automation.
As organizations scale their development efforts, the traditional model of centralized release management becomes a significant bottleneck. We've observed teams spending up to 40% of their time on deployment-related activities that could be automated. The solution lies in building self-service release capabilities that empower development teams while maintaining the governance and security standards that operations teams require.
At VegaStack, we've helped dozens of organizations transform their deployment processes, reducing average release times from hours to minutes while improving reliability and compliance. This guide will walk you through our proven methodology for implementing deployment automation that strikes the perfect balance between developer autonomy and operational control.
The Problem: Release Bottlenecks Are Killing Developer Productivity
The traditional approach to software deployment creates a cascade of inefficiencies that compound as organizations grow. We recently worked with a mid-sized software company where their monthly release cycle required coordination between five different teams, three separate approval processes, and an average of 12 hours of manual work per deployment.
The numbers were staggering: developers spent an average of 8 hours per week on deployment-related tasks, the operations team was overwhelmed with 15-20 deployment requests daily, and the organization was experiencing a 23% increase in deployment failures due to manual errors. More critically, their time-to-market suffered as simple bug fixes took an average of 3.2 days to reach production.
Traditional deployment approaches fail because they treat releases as special events rather than routine operations. Manual handoffs create communication gaps, approval workflows introduce delays that don't add security value, and the lack of standardization means each deployment becomes a unique snowflake requiring individual attention. The result is a system that doesn't scale with business needs and creates friction between development and operations teams.
The fundamental issue isn't just inefficiency - it's the inability to respond quickly to market demands. When deployment becomes a bottleneck, organizations lose their competitive edge and developer satisfaction plummets as teams spend more time fighting process than building features.
Solution Framework: Building Self-Service Deployment Automation
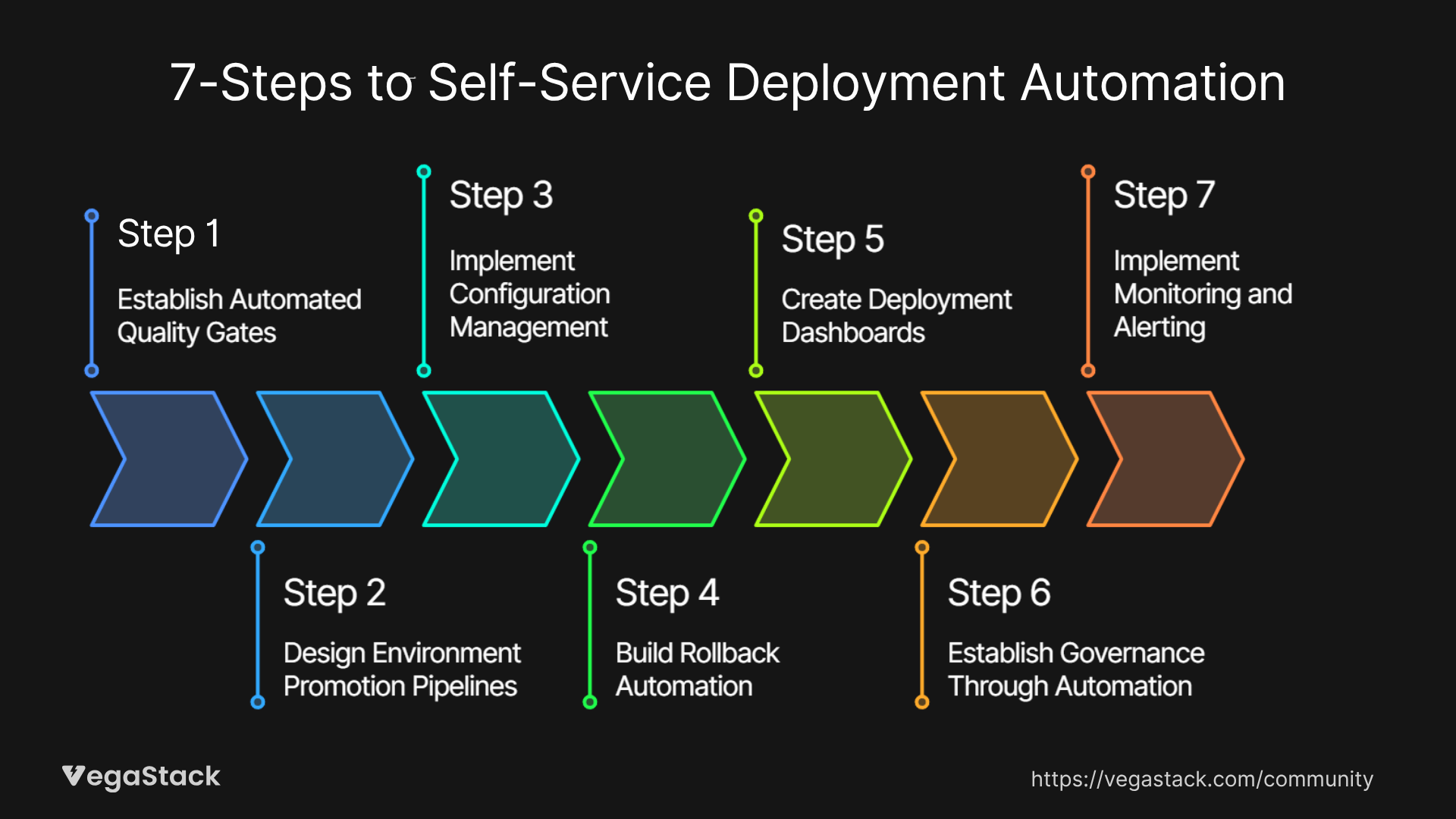
Our approach to deployment automation centers on creating a platform that gives developers the independence they need while embedding the controls that operations teams require. Here's our 7-step methodology for building effective self-service release capabilities:
Step 1: Establish Automated Quality Gates
The foundation of self-service deployment lies in automated quality assurance that eliminates the need for manual reviews. We implement multi-layered validation that includes automated testing, security scanning, performance benchmarking, and compliance checking. These gates act as intelligent guardians that can make the same decisions a human reviewer would make, but in seconds rather than hours.
The key insight here is that most deployment approvals are actually verifying that standard procedures were followed rather than making complex judgment calls. By automating these verifications, we maintain quality while eliminating human bottlenecks.
Step 2: Design Environment Promotion Pipelines
We structure deployments as a series of environment promotions, where code automatically progresses through development, staging, and production environments based on predefined criteria. Each environment serves as a validation checkpoint, with increasingly strict requirements as code approaches production.
This approach ensures that by the time code reaches production, it has been thoroughly tested under conditions that closely mirror the live environment. The pipeline becomes self-managing, requiring human intervention only when automated checks identify genuine issues.
Step 3: Implement Configuration Management
Consistent configuration across environments is critical for reliable deployments. We establish configuration-as-code practices that version control all environment settings, database schemas, infrastructure parameters, and application configurations. This eliminates the "it works on my machine" problem and makes deployments predictable.
The configuration management system also handles secrets management, ensuring that sensitive information like API keys and database passwords are securely injected into applications without exposing them to developers or storing them in version control.
Step 4: Build Rollback Automation
Self-service deployment requires bulletproof rollback capabilities. We implement automated rollback triggers that can revert deployments based on performance metrics, error rates, or manual intervention. The rollback process must be faster and more reliable than the original deployment, often utilizing blue-green deployment strategies or canary releases.
We've learned that teams are more willing to embrace automated deployment when they have confidence in their ability to quickly undo changes. This psychological safety is crucial for adoption.
Step 5: Create Deployment Dashboards
Visibility drives adoption and trust. We build comprehensive dashboards that provide real-time visibility into deployment status, performance metrics, and system health. These dashboards serve both developers who want to track their releases and operations teams who need to monitor overall system stability.
The dashboard becomes the central nervous system of the deployment process, aggregating information from multiple tools and presenting it in a way that enables quick decision-making.
Step 6: Establish Governance Through Automation
Rather than relying on manual approval processes, we embed governance requirements directly into the automation pipeline. This includes automated compliance checking, security vulnerability scanning, performance impact analysis, and change documentation generation.
The governance framework ensures that every deployment meets organizational standards without requiring human gatekeepers. This approach scales infinitely and provides better consistency than manual processes.
Step 7: Implement Monitoring and Alerting
Comprehensive monitoring ensures that automated deployments don't introduce problems that go unnoticed. We establish monitoring that tracks application performance, system resources, error rates, and business metrics. Automated alerting notifies relevant teams when deployments cause degradation in any monitored parameter.
The monitoring system also feeds back into the deployment pipeline, providing data that can be used to improve future releases and identify patterns in deployment success or failure.
Implementation: Orchestrating Complex Dependencies
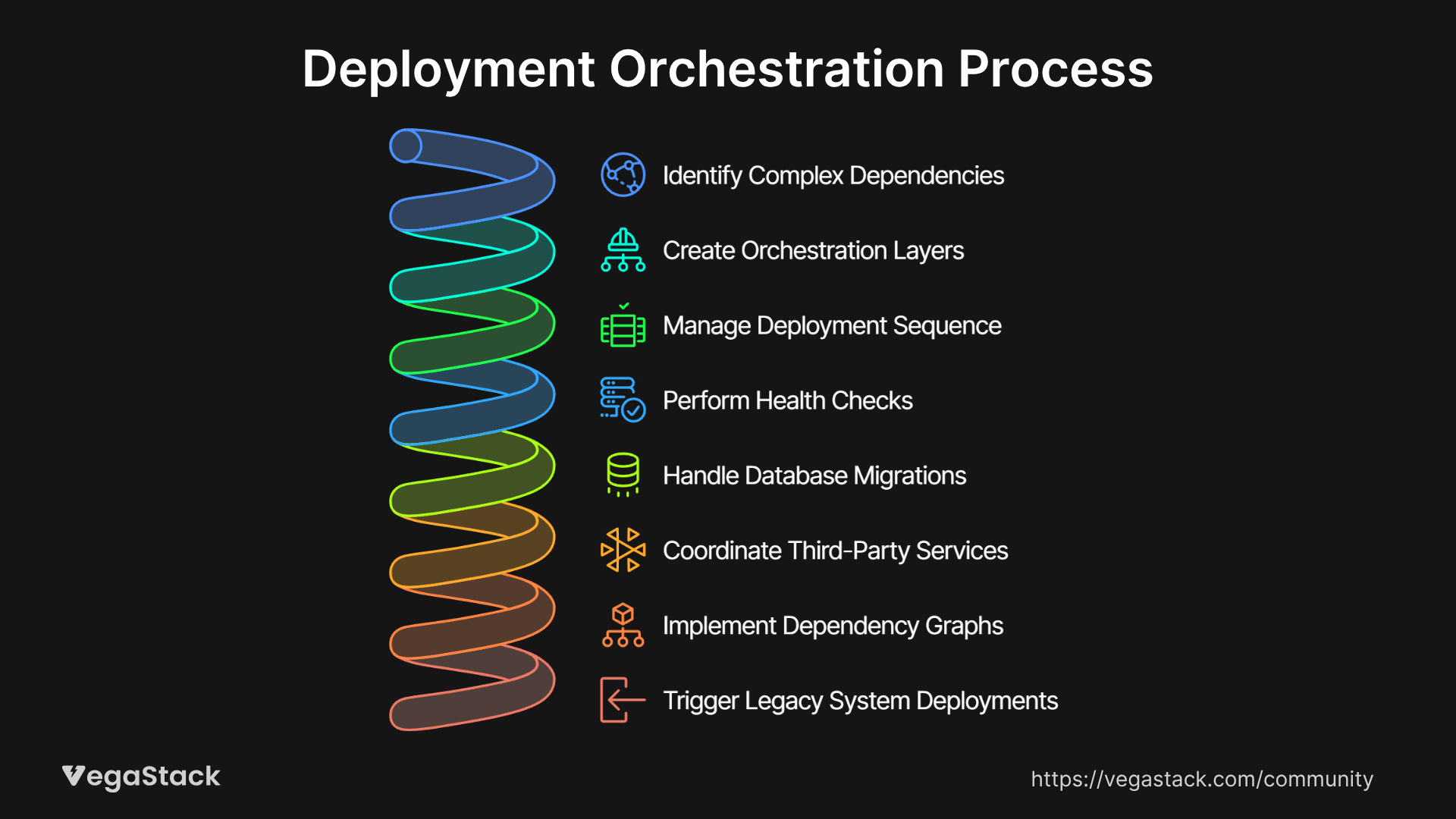
One of the most challenging aspects of deployment automation is handling applications with complex dependencies and coordinated multi-service deployments. We've found that traditional approaches often oversimplify this challenge, leading to automation that works for simple applications but breaks down for real-world enterprise scenarios.
Our solution involves creating deployment orchestration layers that understand service relationships and can coordinate releases across multiple components. This orchestration engine manages the sequence of deployments, waits for health checks to confirm service stability, and can pause or rollback the entire deployment if any component fails to deploy successfully.
The orchestration system also handles database migrations, cache invalidation, and third-party service coordination. We implement sophisticated dependency graphs that map out all the relationships between services and infrastructure components, ensuring that deployments happen in the correct order and that dependent services are properly notified of changes.
For organizations with legacy systems, we often implement hybrid approaches that can trigger deployments on older systems through API calls or scheduled jobs, gradually bringing the entire application portfolio under automation control without requiring massive system rewrites.
Results and Validation: Measuring Success
The impact of implementing self-service deployment automation consistently exceeds expectations. In our recent implementation with a 200-person development organization, we achieved a 78% reduction in average deployment time, from 4.2 hours to 55 minutes. The frequency of deployments increased by 340%, enabling teams to release features and fixes much more responsively.
From a cost perspective, the organization reduced deployment-related operational overhead by approximately $8,400 per month by eliminating manual processes and reducing the time operations staff spent on routine deployments. Developer productivity improved measurably, with teams reporting 25% more time available for feature development rather than deployment management.
The quality metrics were equally impressive: deployment failure rates dropped from 12% to 3%, and the time to recover from failed deployments decreased by 65%. The automated quality gates caught issues that manual reviews had previously missed, particularly around security vulnerabilities and performance regressions.
Perhaps most importantly, developer satisfaction scores improved significantly. Teams reported feeling more empowered and less frustrated with the development process. The operations team also benefited, shifting their focus from routine deployment tasks to higher-value infrastructure optimization and capacity planning activities.
One unexpected benefit was improved compliance posture. The automated governance framework provided better audit trails and more consistent policy enforcement than the previous manual processes had achieved.
Key Learnings and Best Practices
Through numerous implementations, we've identified several fundamental principles that determine the success of deployment automation initiatives:
Start with Culture, Not Technology: The most sophisticated automation won't succeed if teams aren't aligned on the goals and benefits. We've learned to invest significant effort in change management and training, ensuring that both development and operations teams understand how automated deployment serves their interests.
Build Trust Through Transparency: Teams need visibility into what the automation is doing and confidence that they can intervene when necessary. We always implement comprehensive logging, clear status reporting, and easy override mechanisms that allow teams to take manual control when needed.
Embrace Gradual Rollouts: We never implement full automation immediately. Instead, we start with automated deployment to development environments, then staging, and finally production. This phased approach builds confidence and allows us to refine the automation based on real-world usage.
Design for Failure: The most important aspect of deployment automation isn't the happy path - it's how the system behaves when things go wrong. We spend considerable effort on error handling, rollback procedures, and failure notification to ensure that automated deployments fail safely and obviously.
Measure Everything: Successful automation requires comprehensive metrics that go beyond just deployment success rates. We track developer productivity, system reliability, security posture, and business impact to ensure that automation delivers value across all dimensions.
Maintain Human Oversight: While the goal is self-service deployment, we always maintain mechanisms for human oversight and intervention. The operations team shifts from being deployment gatekeepers to being automation shepherds who monitor, maintain, and improve the automated systems.
Conclusion
Deployment automation represents a fundamental shift from treating releases as special events to making them routine operations that happen seamlessly and reliably. By building self-service release capabilities, organizations can dramatically improve their responsiveness to market demands while actually strengthening their governance and security posture.
The key to success lies in understanding that deployment automation isn't just about eliminating manual steps - it's about creating systems that embed organizational knowledge and standards into repeatable, scalable processes. When done correctly, automated deployment becomes a competitive advantage that enables organizations to innovate faster while maintaining the reliability and security that their customers expect.
As you consider implementing deployment automation in your organization, remember that the goal isn't to replace human judgment but to augment it with systems that handle routine decisions automatically and escalate complex situations appropriately.




