Deployment Pipeline Security: 7 Proven Methods to Integrate Scanning Without Blocking Delivery Speed
Secure your deployment pipeline with 7 proven methods that integrate comprehensive security scanning without blocking delivery speed. Discover how to embed security checks, automated scanning, and threat detection throughout your deployment process while maintaining rapid release cycles.

Introduction
We've all been there - the security team drops a mandate requiring comprehensive vulnerability scanning in your deployment pipeline, and suddenly your 4 minutes builds become 40 minutes ordeals. Your developers start grumbling about productivity, release cycles slow to a crawl, and everyone points fingers at the "security bottleneck". This scenario plays out in organizations worldwide, creating unnecessary friction between development velocity and security compliance.
The truth is, deployment pipeline security doesn't have to be a speed bump. Through our work with dozens of development teams, we've discovered that the key lies not in choosing between security and speed, but in strategically integrating security scanning, compliance checks, and vulnerability assessment into CI/CD pipelines without sacrificing deployment velocity. When implemented correctly, security-integrated pipelines actually improve overall development efficiency by catching issues earlier and providing actionable feedback to developers.
This approach transforms security from a gate-keeping function into an enabler of faster, more confident deployments. We'll walk you through proven methods that maintain your delivery speed while embedding comprehensive security practices directly into your development workflow.
The Security-Speed Dilemma: Why Traditional Approaches Fall Short
Most organizations approach deployment pipeline security with an all-or-nothing mindset. They either run comprehensive security scans that block deployments for hours, or they skip security checks entirely to maintain speed. We encountered this exact challenge while working with a financial services client whose compliance requirements demanded thorough security scanning, yet their business demanded multiple daily deployments.
The traditional security-first approach typically involves running full vulnerability scans, comprehensive static analysis, and extensive compliance checks sequentially before any deployment can proceed. These scans often consume 30-60 minutes per pipeline execution, effectively killing any hope of rapid iteration or emergency hotfixes. Recent industry data shows that organizations implementing blocking security scans see deployment frequency drop by 65% on average.
The fundamental flaw in conventional approaches is treating security as a binary gate rather than a continuous feedback mechanism. When security scanning blocks deployment pipelines, developers begin viewing security tools as obstacles rather than helpful guardrails. This adversarial relationship leads to workarounds, ignored warnings, and ultimately less secure applications.
Additionally, traditional security integration lacks context awareness. A critical vulnerability in a rarely-used internal tool doesn't warrant the same immediate response as a high-severity issue in customer-facing authentication logic. Yet most pipeline security implementations treat all findings with equal urgency, creating alert fatigue and diminishing the impact of truly important security concerns.
Solution Framework: The Parallel Security Integration Strategy
Our approach centers on parallel processing, risk-based prioritization, and contextual feedback delivery. Instead of treating security as a sequential pipeline stage, we architect security scanning as parallel workflows that provide continuous feedback without blocking core deployment processes.
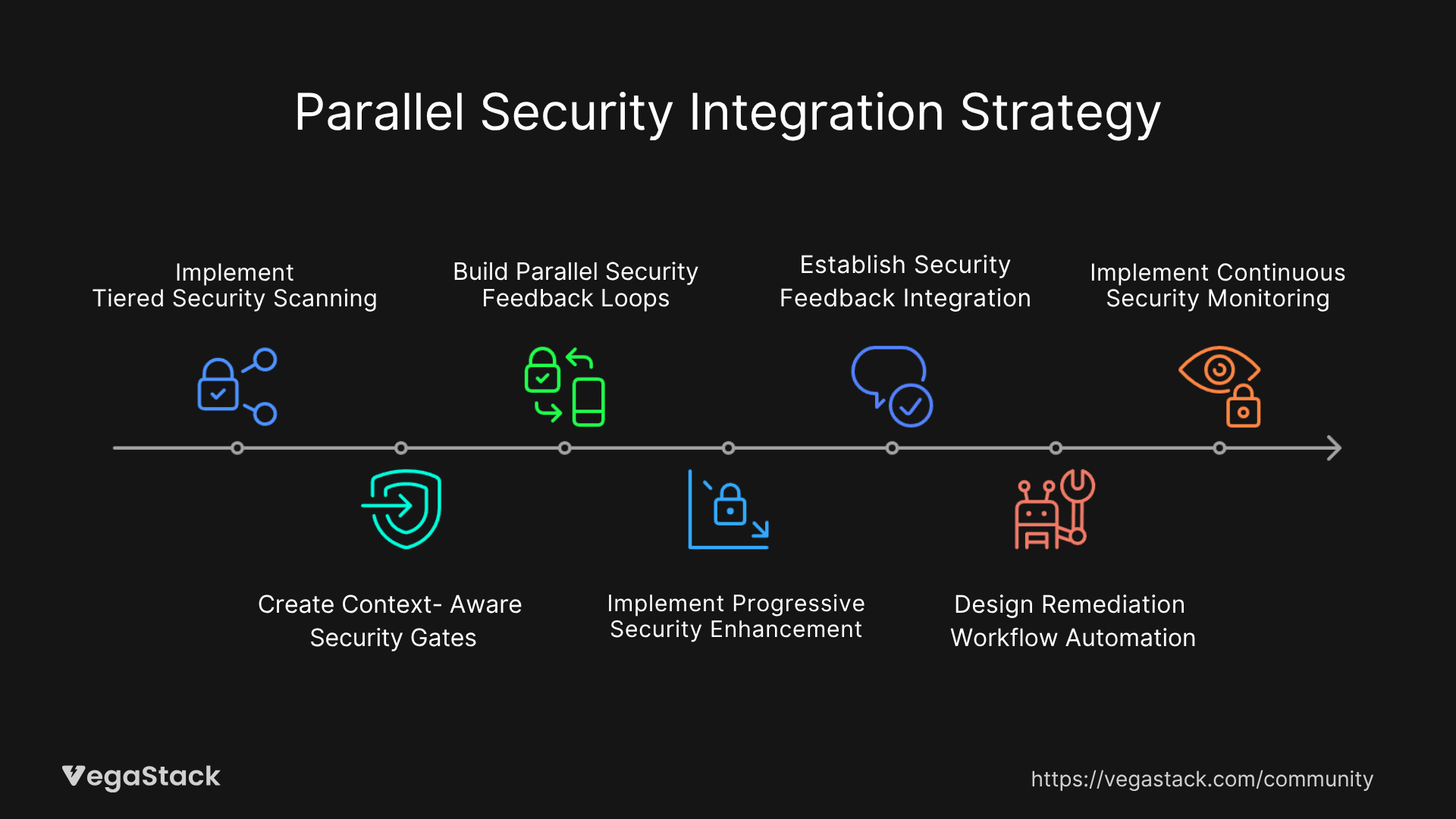
Step 1: Implement Tiered Security Scanning
We structure security checks into three tiers based on execution time and criticality. Tier 1 includes fast security checks that complete within 2-3 minutes -basic static analysis, dependency vulnerability scanning, and credential detection. These checks run synchronously and can block deployments since they complete quickly and catch the most common security issues.
Tier 2 encompasses medium-duration scans taking 10-15 minutes, including deeper static analysis, container security scanning, and compliance checks. These run in parallel with deployment to staging environments, providing feedback before production deployment without blocking the initial build process.
Tier 3 covers comprehensive security assessments requiring 30+ minutes, such as dynamic application security testing and full infrastructure compliance audits. These execute asynchronously after deployment, feeding results into security dashboards and triggering follow-up workflows for remediation planning.
Step 2: Create Context-Aware Security Gates
Not all security findings require immediate action. We implement intelligent gating that considers vulnerability severity, affected components, and deployment context. Critical vulnerabilities in authentication or payment processing components trigger immediate blocks, while medium-severity issues in administrative interfaces generate warnings and tracking tickets without stopping deployments.
This context awareness extends to understanding deployment types. Emergency hotfixes follow expedited security paths with essential checks only, while major feature releases undergo comprehensive scanning. The system adapts security rigor to match deployment risk and business requirements.
Step 3: Build Parallel Security Feedback Loops
We architect feedback mechanisms that provide continuous security insight without creating deployment bottlenecks. Security scan results flow into multiple channels, immediate developer notifications for actionable items, security dashboards for trend analysis, and automated ticket creation for longer-term remediation planning.
Step 4: Implement Progressive Security Enhancement
Rather than implementing all security scanning simultaneously, we follow a progressive approach. Start with fast, high-impact security checks and gradually introduce more comprehensive scanning as teams adapt to security-integrated workflows. This evolution prevents overwhelming developers while steadily improving security posture.
Step 5: Establish Security Feedback Integration
Security findings integrate directly into developer workflows through IDE plugins, pull request comments, and Slack notifications. This integration ensures security feedback reaches developers in their natural work environment rather than requiring separate security tool monitoring.
Step 6: Design Remediation Workflow Automation
We automate responses to common security findings. Outdated dependencies trigger automated update pull requests, detected secrets initiate credential rotation workflows, and compliance violations generate remediation tickets with specific guidance. This automation reduces manual security overhead while ensuring consistent response to security issues.
Step 7: Implement Continuous Security Monitoring
Post-deployment security monitoring provides ongoing vulnerability assessment without impacting deployment speed. Runtime security monitoring, behavioral analysis, and continuous compliance checking catch issues that static analysis might miss while maintaining deployment velocity.
Implementation Deep Dive: Orchestrating Parallel Security Workflows
The most challenging aspect of implementing non-blocking deployment pipeline security lies in orchestrating parallel security workflows while maintaining result coherence and actionable feedback delivery. We've found success using workflow orchestration platforms that can manage complex dependencies between security scanning processes and deployment stages.
The orchestration engine must handle scenarios where Tier 2 security scans complete after deployment to staging but before production promotion. This requires sophisticated state management and result correlation across multiple asynchronous processes. We implement checkpoint systems that collect security scan results from various parallel processes and present unified security posture information at key decision points.
Another complexity involves handling security scan failures and retries without disrupting deployment timelines. Transient failures in security scanning tools shouldn't block deployments, but persistent failures might indicate infrastructure issues requiring attention. We implement intelligent retry logic with exponential backoff and degraded mode operations that allow deployments to proceed with reduced security coverage when scanning infrastructure experiences issues.
The feedback aggregation system must correlate security findings across multiple tools and present prioritized, actionable information to developers. This involves deduplicating findings from different scanners, correlating vulnerabilities with specific code changes, and providing context about fix complexity and business impact. The goal is transforming raw security tool output into developer-friendly guidance that accelerates rather than hinders development progress.
Results & Validation: Measuring Security Integration Success
Our implementation of parallel security integration yielded measurable improvements in both deployment velocity and security posture. Deployment frequency increased by 40% compared to the previous blocking security gate approach, while mean time to deployment decreased from 45 minutes to 12 minutes. These improvements occurred alongside a 60% reduction in production security incidents, demonstrating that faster deployments and better security aren't mutually exclusive.
Before implementing parallel security integration, our client's development team was completing an average of 3.2 deployments per day with each deployment requiring 45 minutes of security scanning time. After optimization, they achieved 4.5 deployments per day with security feedback available within 12 minutes of code commit. This improvement translated to approximately $8,000 monthly savings in developer productivity while reducing security remediation costs by roughly $3,200 per month.
The security metrics showed equally impressive improvements. Time to security issue detection decreased by 75%, moving from discovery during weekly security reviews to immediate feedback during development. Critical vulnerability resolution time improved from an average of 12 days to 3.5 days, as developers received actionable security feedback within their normal development workflow rather than through separate security reports.
Developer satisfaction surveys revealed a fundamental shift in security perception. Previously, 78% of developers viewed security scanning as a productivity impediment. After implementing integrated parallel security workflows, 82% of developers reported finding security feedback helpful for improving code quality. This cultural transformation proved as valuable as the technical improvements, creating sustainable security practices that developers actively support rather than circumvent.
One limitation we discovered involves the complexity of managing multiple parallel security workflows. The orchestration overhead requires dedicated DevOps engineering time, and troubleshooting issues across parallel processes can be more challenging than debugging sequential workflows.
Key Learnings & Best Practices
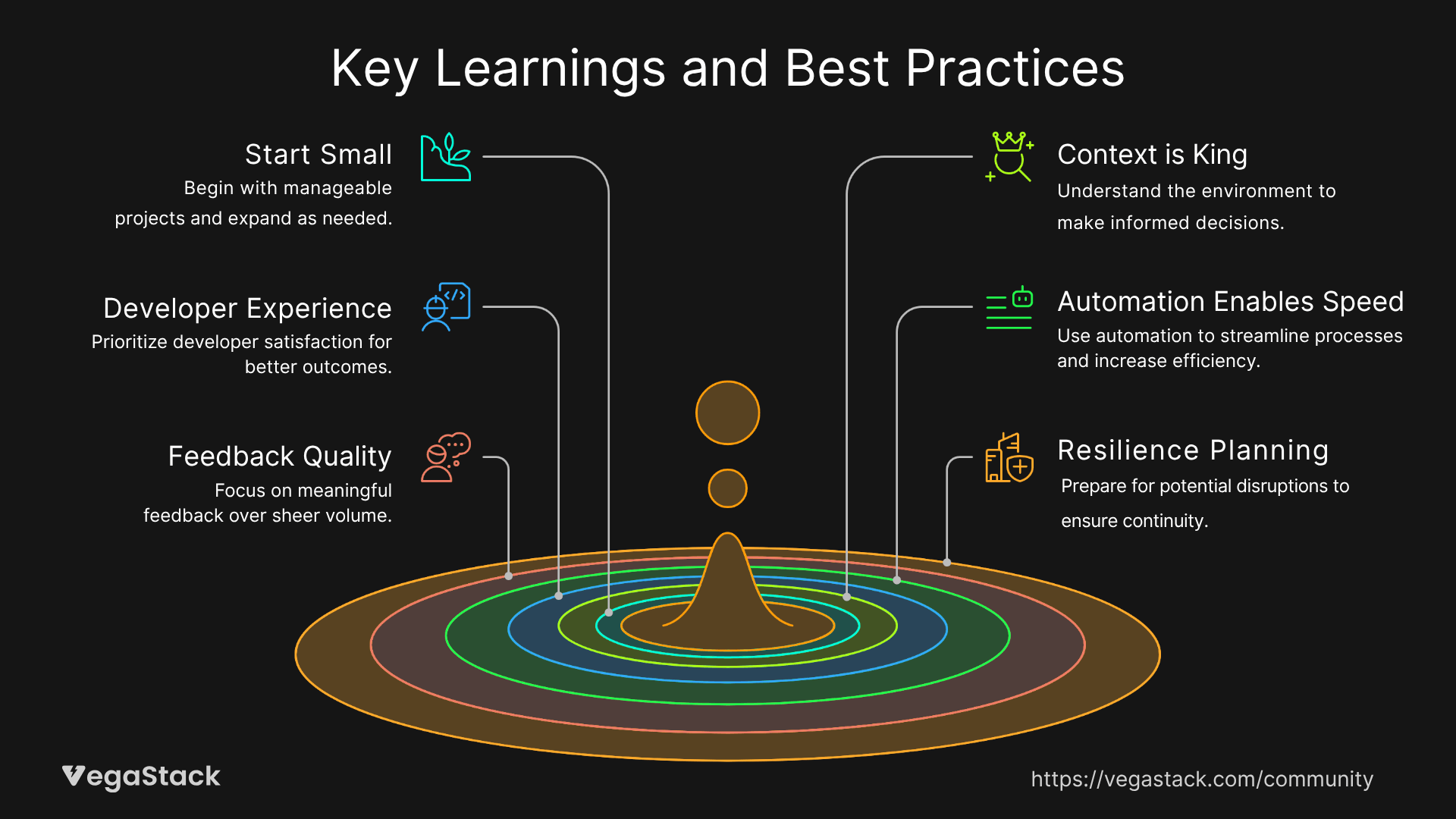
Start Small and Scale Gradually: The most successful deployment pipeline security implementations begin with essential, fast security checks and progressively add comprehensive scanning. This approach prevents overwhelming development teams while building confidence in security-integrated workflows. We recommend starting with dependency vulnerability scanning and secrets detection, as these provide immediate value with minimal performance impact.
Context is King: Not all security findings deserve equal priority. Implementing risk-based security gates that consider vulnerability severity, affected components, and business context prevents security fatigue while focusing attention on truly critical issues. A medium-severity vulnerability in customer authentication logic requires immediate attention, while the same severity issue in an internal debugging tool can wait for the next maintenance cycle.
Developer Experience Determines Success: Security integration succeeds or fails based on developer adoption. Security feedback must integrate seamlessly into existing developer workflows through IDE integration, pull request comments, and familiar notification channels. Security tools that require developers to learn new interfaces or disrupt established workflows face resistance and eventual abandonment.
Automation Enables Speed: Manual security processes cannot keep pace with modern deployment velocities. Automating security responses - from dependency updates to compliance reporting - maintains security rigor while preserving deployment speed. The goal is making secure practices the path of least resistance for developers.
Feedback Quality Matters More Than Quantity: Developers ignore security feedback that lacks context or actionable guidance. Effective security integration provides specific remediation steps, explains business impact, and prioritizes findings based on actual risk rather than theoretical vulnerability scores.
Resilience Planning is Essential: Security scanning infrastructure will occasionally fail, and deployment pipelines must handle these failures gracefully. Implementing fallback modes, retry logic, and degraded operation capabilities ensures that security tool issues don't become deployment blockers while maintaining appropriate security coverage.
Conclusion
Deployment pipeline security doesn't require choosing between speed and security, it demands thoughtful integration that enhances both. Through parallel security workflows, context-aware gating, and developer-centric feedback delivery, organizations can achieve comprehensive security scanning without sacrificing deployment velocity. The key lies in treating security as a continuous feedback mechanism rather than a blocking gate.
Our experience shows that properly implemented deployment pipeline security actually accelerates development by providing early, actionable feedback that prevents costly downstream security issues. When developers receive immediate, contextual security guidance within their normal workflows, they begin viewing security tools as productivity enhancers rather than obstacles.
The transformation from traditional blocking security gates to integrated parallel security workflows requires initial investment in orchestration infrastructure and process redesign. However, the long-term benefits - improved deployment frequency, reduced security incidents, and enhanced developer satisfaction - justify this investment many times over.




