How to Fix HashiCorp Vault Authentication Failures in DevOps Workflows
Learn how to troubleshoot and fix HashiCorp Vault authentication failures in your DevOps pipelines. This practical guide covers common auth issues, token management problems, and access configuration errors. Get proven solutions for maintaining secure, reliable Vault authentication in production.

Quick Solution Summary
HashiCorp Vault authentication failures in automated workflows stem from four main issues: expired or misconfigured tokens, incorrect authentication method setup, network connectivity problems, and high availability configuration gaps. Fix these by verifying token status with checking authentication method configurations, ensuring proper network access, and implementing redundant Vault instances with load balancing.
Introduction
You're in the middle of a deployment when your CI/CD pipeline suddenly fails with "authentication failed" errors from HashiCorp Vault. Sound familiar? This issue hits DevOps teams hard because it breaks automated workflows right when you need them most.
Vault authentication failures don't just slow down deployments, they can force teams to use less secure workarounds or manual processes that introduce risk. The frustrating part? These failures often appear intermittent, making them tough to diagnose and fix permanently.
Here's the reality: most Vault authentication issues aren't actually about wrong passwords. They're about token lifecycle management, authentication method configuration, network connectivity, and high availability setup. We'll walk through each problem area and show you exactly how to fix them.
Problem Context & Common Symptoms
When Authentication Failures Strike
Vault authentication failures typically surface in automated environments, GitLab CI/CD pipelines, Jenkins jobs, Bamboo workflows, and Kubernetes deployments. These failures hit hardest during peak deployment times when multiple workflows compete for Vault resources.
The issue manifests differently across environments. In AWS-based setups, you might see IAM role assumption failures. In Kubernetes environments, service account authentication can break unexpectedly. On-premise installations often struggle with network connectivity and certificate validation.
Recognizing the Warning Signs
Primary symptoms include intermittent "authentication failed" messages in automation logs, workflows that worked yesterday but fail today, and authentication errors that resolve themselves after manual intervention. You'll also notice increased error rates during scaling events or after infrastructure changes.
Secondary indicators include longer workflow execution times, increased manual intervention requirements, and teams reporting that they have to "retry" deployments multiple times before success. Performance impacts show up as delayed releases, increased mean time to recovery, and frustrated development teams.
Common Error Patterns
Error messages vary by authentication method but typically include generic "authentication failed" responses, token expiration warnings, and permission denied errors. AWS IAM authentication failures often mention role assumption problems, while Kubernetes authentication shows service account validation errors.
Root Cause Analysis: Why Vault Authentication Really Fails
The Real Technical Culprits
Most authentication failures trace back to token lifecycle mismanagement. Teams set up tokens without considering expiration times, renewal processes, or proper rotation schedules. When tokens expire during long-running workflows, authentication breaks mid-process.
Authentication method misconfiguration ranks as the second major cause. AWS IAM auth methods fail when roles lack proper trust relationships or when instance profiles don't match expected configurations. Kubernetes authentication breaks when service accounts don't have correct role bindings or when cluster certificates change.
Network connectivity issues cause intermittent failures that look like authentication problems. Firewall rules, DNS resolution delays, and load balancer health checks can all interrupt Vault communication. These network hiccups create the "works sometimes, fails others" pattern that makes troubleshooting difficult.
Configuration Traps That Catch Teams
High availability setups introduce their own authentication challenges. When Vault instances aren't properly synchronized or when load balancers don't handle session affinity correctly, authentication tokens become invalid across different cluster nodes.
Resource constraints create authentication timeouts that appear as credential failures. Vault instances running low on CPU or memory respond slowly to authentication requests, causing automation tools to timeout and retry with failed results.
Why Standard Solutions Miss the Mark
Teams often focus on credential verification when authentication fails, but credentials aren't usually the problem. The real issues lie in environmental factors, network connectivity, resource availability, and configuration synchronization across distributed systems.
Simply retrying authentication attempts doesn't address underlying token expiration or network connectivity issues. Without fixing root causes, these "solutions" just delay the next failure.
Step-by-Step Solution: Complete Vault Authentication Fix
Prerequisites and Preparation
Before troubleshooting, ensure you have administrative access to both Vault and your automation tools. You'll need the Vault CLI installed and configured with appropriate permissions to examine tokens and authentication methods.
Back up your current Vault configuration and automation scripts. Document existing authentication flows and note any recent changes to infrastructure, network configurations, or Vault policies.
Primary Solution Approach
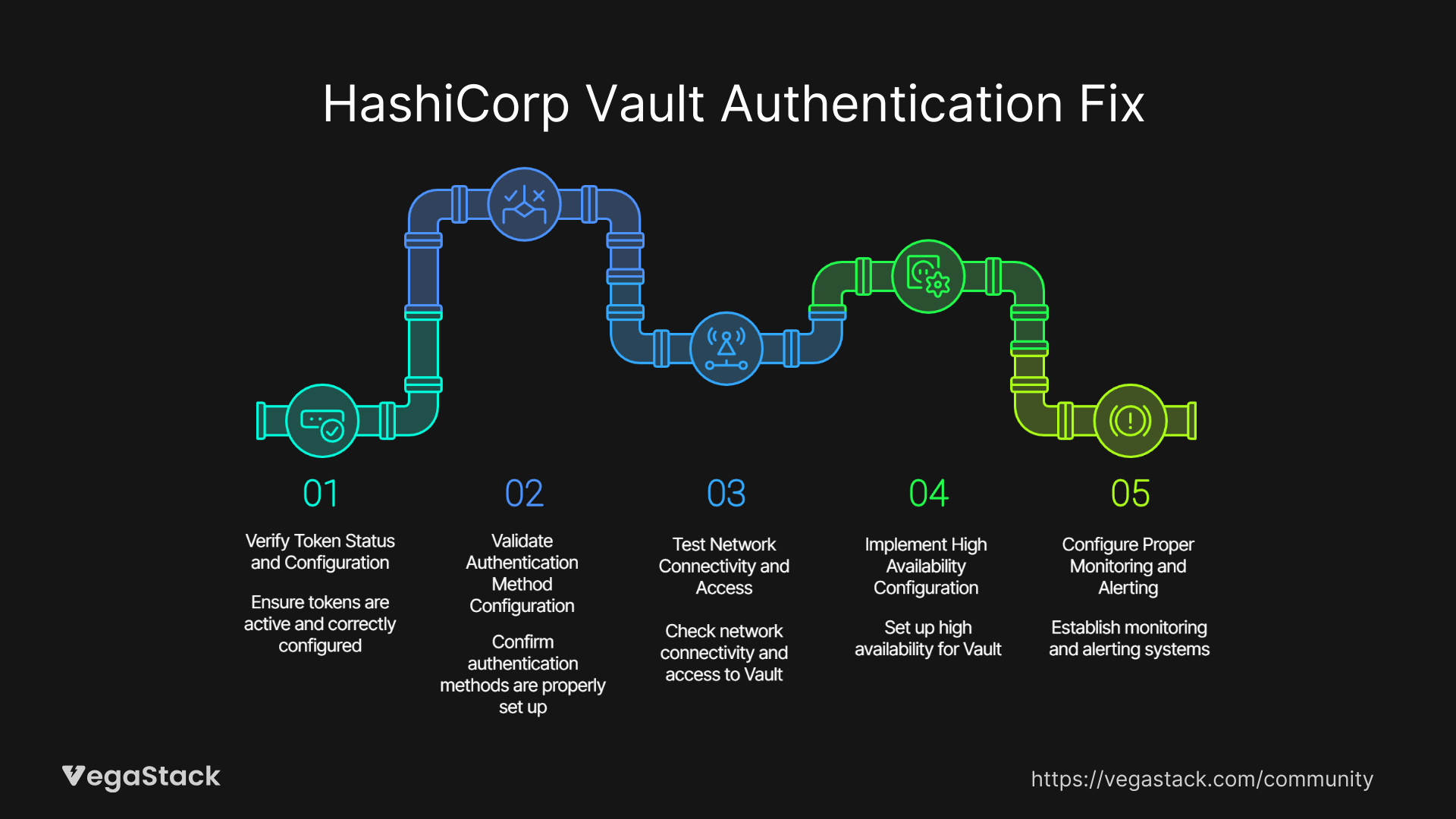
Step 1: Verify Token Status and Configuration
Start with token verification using the Vault CLI. Run to check current token status, expiration time, and associated policies or automation workflows, examine token creation parameters and renewal policies.
Check token TTL settings against workflow execution times. If workflows run longer than token lifespans, authentication will fail mid-process. Adjust token TTL or implement token renewal in your automation scripts.
Step 2: Validate Authentication Method Configuration
Review your authentication method setup thoroughly. For AWS IAM authentication, verify that IAM roles have proper trust relationships and that instance profiles match Vault configuration expectations.
For Kubernetes authentication, confirm service account configurations and role bindings. Check that cluster certificates haven't changed and that service account tokens are being mounted correctly in pods.
Step 3: Test Network Connectivity and Access
Verify network connectivity between automation tools and Vault instances. Test DNS resolution, firewall rules, and load balancer configurations. Use network troubleshooting tools to identify connectivity issues that might cause intermittent failures.
Check Vault server logs for connection errors, timeout messages, or certificate validation failures. These logs often reveal network-related issues that appear as authentication problems.
Step 4: Implement High Availability Configuration
Set up multiple Vault instances for redundancy if you haven't already. Configure load balancers to distribute traffic across healthy Vault nodes with proper health checks and session affinity settings.
Ensure Vault cluster synchronization works correctly. Test failover scenarios to verify that authentication continues working when individual Vault instances become unavailable.
Step 5: Configure Proper Monitoring and Alerting
Implement comprehensive logging for authentication attempts, token lifecycle events, and system performance metrics. Set up alerts for authentication failure rates, token expiration warnings, and Vault instance health status.
Alternative Solutions for Specific Environments
AWS Environment Workarounds
For AWS deployments, consider using EC2 instance metadata for authentication where possible. This approach reduces dependency on manually managed credentials and provides more reliable authentication for EC2-based workflows.
Configure AWS IAM roles with appropriate trust policies and minimal required permissions. Use temporary credentials with automatic rotation to reduce long-term credential exposure risks.
Kubernetes-Specific Solutions
In Kubernetes environments, implement service account token volume projection for improved security and reliability. Configure token refresh mechanisms to handle long-running pod authentication requirements.
Use Kubernetes secrets management integration with Vault to streamline credential handling and reduce manual token management overhead.
Solution Validation and Testing
Test your fixes thoroughly before deploying to production. Create test workflows that simulate your production authentication patterns and verify they work consistently across different Vault instances.
Monitor authentication success rates and response times after implementing fixes. Set up automated testing to catch authentication regressions before they impact production workflows.
Troubleshooting Common Implementation Issues
Configuration Errors and Fixes
Authentication Method Misconfigurations
The most common implementation issue involves incorrect authentication method parameters. AWS IAM authentication fails when bound IAM roles don't match actual instance roles or when region settings don't align with Vault configuration.
For Kubernetes authentication, verify that bound service account names and namespaces match your pod configurations exactly. Case sensitivity and namespace specification often cause authentication failures.
Network and Connectivity Problems
Load balancer health checks can interfere with Vault authentication if not configured properly. Ensure health check endpoints don't conflict with authentication paths and that load balancer timeout settings accommodate Vault response times.
Certificate validation errors occur when Vault instances use self-signed certificates or when certificate chains aren't properly configured. Verify certificate validity and ensure automation tools can validate the full certificate chain.
Permission and Access Issues
Insufficient Vault Policies
Authentication might succeed but authorization fails due to restrictive Vault policies. Review policy assignments for authentication methods and ensure they provide necessary permissions for your automation workflows.
Check that policies include required capabilities for secret access, token renewal, and any administrative functions your automation requires.
Role Binding Problems
AWS IAM roles need proper trust relationships with Vault and sufficient permissions for required operations. Verify that roles can be assumed by your automation environments and that they include necessary AWS service permissions.
Kubernetes role bindings must connect service accounts to appropriate cluster roles or role bindings. Missing bindings cause authentication to succeed but authorization to fail.
Edge Cases and Special Scenarios
Multi-Region Deployments
Cross-region authentication introduces latency and potential connectivity issues. Consider regional Vault deployments or ensure network connectivity supports cross-region authentication latency requirements.
Legacy System Integration
Older automation tools might not support modern authentication methods or proper token handling. Implement authentication proxies or consider upgrading automation tooling to support current Vault authentication best practices.
Prevention Strategies and Long-Term Optimization
Proactive Authentication Management
Token Lifecycle Automation
Implement automated token renewal processes in your workflows. Don't rely on manual token management or long-lived tokens that create security risks. Use short-lived tokens with automatic renewal mechanisms.
Set up token expiration monitoring and alerts. Know when tokens will expire before they impact production workflows. Implement graceful token renewal that doesn't interrupt running processes.
Authentication Method Standardization
Standardize authentication methods across your organization. Avoid mixing multiple authentication approaches unless necessary. Consistent authentication methods reduce complexity and troubleshooting overhead.
Document authentication configurations and maintain them as code. Use infrastructure as code tools to manage Vault authentication method configurations and ensure consistency across environments.
Monitoring and Early Detection
Comprehensive Logging Strategy
Implement detailed logging for all authentication events. Log successful authentications, failures, token renewals, and policy evaluations. This information becomes critical for troubleshooting future issues.
Set up log aggregation and analysis to identify patterns in authentication failures. Look for correlations between failures and infrastructure changes, deployment events, or resource utilization spikes.
Performance Monitoring
Monitor Vault authentication performance metrics including response times, success rates, and resource utilization. Set up alerts for degraded performance that might indicate impending authentication failures.
Track authentication patterns and usage trends. Understanding normal authentication behavior helps identify anomalies that might indicate configuration problems or security issues.
Long-Term Reliability Improvements
High Availability Architecture
Design Vault deployments for high availability from the start. Use multiple Vault instances across availability zones or regions. Implement proper cluster configuration with automated failover capabilities.
Regularly test disaster recovery scenarios including Vault cluster failures, network partitions, and data center outages. Verify that authentication continues working during various failure conditions.
Capacity Planning
Plan Vault capacity based on authentication load patterns. Consider peak usage times, scaling events, and growth projections. Insufficient capacity causes authentication timeouts that appear as credential failures.
Implement auto-scaling for Vault instances where possible. Use load balancing and health checks to distribute authentication load across available instances.

Related Issues and Extended Solutions
Connected Problems
CI/CD Pipeline Reliability
Vault authentication failures directly impact CI/CD pipeline reliability. Implement pipeline retry logic with exponential backoff for authentication failures. Design pipelines to handle temporary authentication issues gracefully.
Consider circuit breaker patterns for Vault integration. If authentication failures reach threshold levels, switch to degraded functionality rather than complete pipeline failures.
Kubernetes Deployment Challenges
Kubernetes deployments often fail when pods can't authenticate to Vault during startup. Implement init containers for Vault authentication or use sidecar patterns for ongoing credential management.
Use Kubernetes operators that understand Vault integration patterns. These operators can handle authentication complexity and provide better error handling for Vault-related failures.
Advanced Optimization Techniques
Caching and Performance
Implement authentication caching where appropriate to reduce Vault load and improve response times. Be careful with cache TTL settings to avoid using expired credentials.
Use connection pooling for Vault clients to reduce connection overhead. Configure appropriate connection limits and timeouts based on your usage patterns.
Security Hardening
Implement authentication audit logging for compliance and security monitoring. Track authentication patterns to identify potential security issues or misuse.
Use shortest possible token lifespans while maintaining operational efficiency. Implement just-in-time credential provisioning where possible to reduce credential exposure time.
Conclusion and Next Steps
Vault authentication failures in DevOps workflows stem from predictable causes: token lifecycle issues, authentication method misconfigurations, network connectivity problems, and high availability gaps. The solution involves systematic verification of each component followed by proper monitoring and prevention strategies.
Start by implementing comprehensive token management with appropriate TTL settings and renewal processes. Fix authentication method configurations and ensure network connectivity supports your usage patterns. Then implement high availability architecture with proper load balancing and failover capabilities.
Set up monitoring and alerting before you need them. Authentication failures often cascade quickly, so early detection prevents widespread workflow disruptions. Regular testing of authentication systems helps catch issues before they impact production deployments.
The key to long-term success lies in treating Vault authentication as a critical infrastructure component that requires proper planning, monitoring, and maintenance. Teams that invest in robust authentication architecture see dramatically reduced failure rates and faster recovery times when issues do occur.
Monitor your authentication success rates after implementing these fixes. Most teams see improvement within hours of addressing configuration issues and sustained reliability improvements once proper monitoring and high availability measures are in place.




