How to Fix Visual Testing Baseline Management Issues
Learn how to solve visual testing baseline management challenges. This practical guide covers handling screenshot differences, managing baseline updates, and reducing false positives. Get proven techniques for maintaining stable visual tests.

Quick Solution
The fix: Implement a controlled baseline approval workflow where baseline images only update after manual review and approval, use AI-powered comparison instead of pixel-by-pixel matching, and store baselines under version control with proper ignore regions for dynamic content. This reduces false positives by up to 70% and eliminates the noise from outdated baseline images in your visual regression testing pipeline.
Introduction
You're running visual regression tests in your CI/CD pipeline, and everything seems fine until suddenly you're drowning in false positives. Your test results show dozens of visual differences, but when you check the actual UI, nothing's wrong. The real issue? Your baseline images are outdated and no longer match your current design.
This problem hits development teams hard, especially those pushing frequent UI updates. Instead of catching real regressions, your visual testing becomes a maintenance nightmare that slows down deployments and frustrates developers. The baseline management issue affects popular tools like Applitools, Percy, BackstopJS, and any Selenium-based visual testing setup.
Here's how we'll solve this: establish reliable baseline management practices, implement smart comparison methods, and set up approval workflows that keep your visual tests accurate without the constant noise. We've seen teams cut their false failure rates by 70% using these methods.
Problem Context & Symptoms
Visual testing baseline management issues typically surface during active development phases when UI changes happen frequently. Your CI/CD pipeline runs visual tests automatically, but the baseline images haven't kept up with legitimate design changes, causing chaos in your test results.
Common symptoms include frequent test failures showing visual differences when no actual regressions exist, diff images displaying clear mismatches between outdated baselines and current UI, and an increasing number of baseline update prompts that never seem to stabilize your test results. You'll notice slower feedback cycles because your team spends more time investigating false positives than fixing real issues.
The warning signs are unmistakable: increased noise in test results after UI deployments, repeated baseline update cycles that don't resolve the underlying problem, and growing test execution times as your pipeline handles more visual diffs. Your logs show visual mismatches, but manual testing reveals no actual defects.
This problem particularly affects teams using continuous integration with frequent UI updates, feature flags, or A/B testing scenarios. The issue spans across operating systems and browser environments, but it's most problematic in cloud infrastructures where CI/CD pipelines run automatically on every build.
Root Cause Analysis
The technical root causes behind baseline management issues stem from several key factors. Baselines get updated automatically or prematurely, creating inconsistencies between what the test expects and what the UI actually displays. When baseline images are captured at a fixed point in time, they become obsolete as the UI evolves through normal development cycles.
Over-sensitive pixel-by-pixel comparison methods generate excessive noise due to minor rendering differences, anti-aliasing variations, or browser-specific display characteristics. Many teams lack environment-controlled rendering, leading to non-deterministic screenshots that vary between test runs even when nothing has changed.
Poor version control practices for baseline image management compound the problem. Teams often store baselines outside their main repository or fail to implement proper review workflows for baseline updates. This creates a disconnect between code changes and visual expectations.
Common trigger scenarios include frequent visual UI changes pushed directly into main branches, automated CI/CD pipelines running visual tests without conditional baseline updates, and browser or operating system updates that change rendering outputs. Changes in fonts, colors, or layout decisions that aren't reflected in baselines create immediate mismatches.
Standard solutions fail because teams often have the misconception that baselines should update automatically after every test run, which leads to degraded baseline quality. Blindly accepting all detected changes overwhelms the baseline management process, while ignoring dynamic content areas produces noisy false positives that mask real issues.
Step-by-Step Solution
Prerequisites and Preparation
Before implementing the solution, ensure you have access to your source code repository with baseline images, a configured CI/CD pipeline running visual regression tests, and permissions for environment setup and baseline approval workflows. Back up your existing baseline images and test artifacts before making changes, and verify your test environment matches production UI rendering conditions.
Primary Solution Implementation
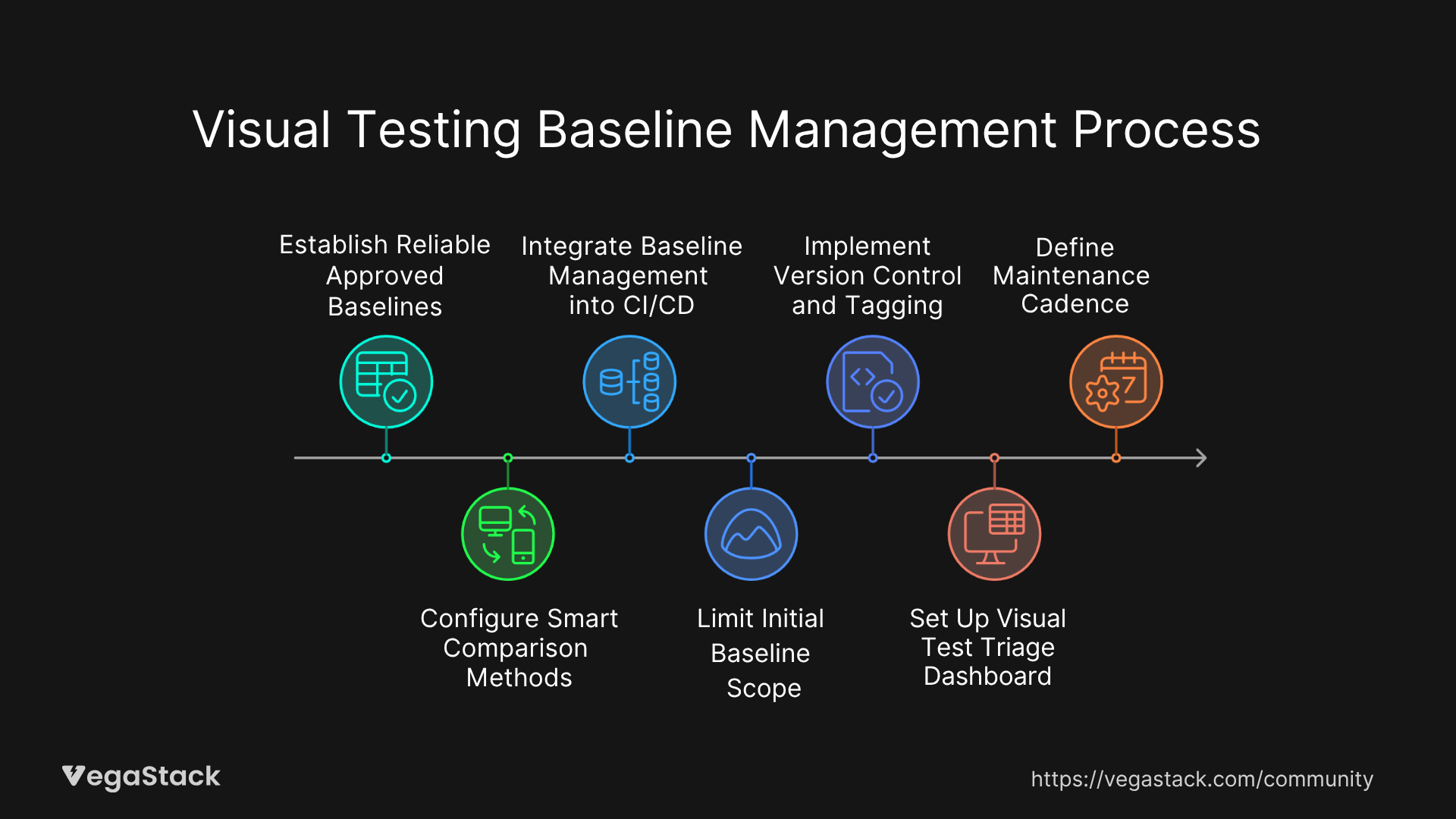
Step 1: Establish Reliable Approved Baselines
Start by capturing a complete set of baseline images through a full UI walkthrough. Run this process manually or automatically, but ensure it covers all critical user journeys and UI components. Review each captured baseline image and approve them as golden masters. This creates your foundation for accurate visual comparisons.
Step 2: Configure Smart Comparison Methods
Switch from pixel-by-pixel comparison to AI-powered or DOM-based comparison methods. Most modern visual testing tools like Applitools offer AI comparison that reduces noise from minor rendering differences. Configure ignore annotations for dynamic areas like timestamps, user-specific content, or animated elements that change between test runs.
Step 3: Integrate Baseline Management into CI/CD
Set up your pipeline so baseline updates only occur on explicit approval. Implement this through pull request reviews for visual diffs, where developers and QA team members can review proposed baseline changes before they're accepted. This prevents automatic updates that degrade baseline quality.
Step 4: Limit Initial Baseline Scope
Focus on critical user journeys and the most impactful UI components first. Don't try to capture every possible screen variation initially. Start with login flows, checkout processes, and primary navigation elements. Expand coverage gradually as your baseline management process stabilizes.
Step 5: Implement Version Control and Tagging
Store baseline images in Git or dedicated artifact repositories with full traceability to UI versions. Tag baselines with release versions or feature branches so you can track which baseline corresponds to which UI state. This enables rollback capabilities when baseline updates cause problems.
Step 6: Set Up Visual Test Triage Dashboard
Configure alerts and dashboards that help you quickly identify intentional versus unintentional visual differences. Most visual testing platforms provide diff severity scoring and component-level change tracking. Use these features to prioritize which differences need immediate attention.
Step 7: Define Maintenance Cadence
Schedule regular baseline reviews aligned with your release cycles. Plan baseline updates during feature freeze periods or before major releases when UI changes are intentional and approved. This prevents baseline drift during active development periods.
The initial baseline setup typically takes one to three days depending on application size, while integration and configuration tuning requires an additional one to two days. Ongoing maintenance integrates into daily workflows once established.
Alternative Solutions
If the primary approach doesn't fit your environment, consider manual baseline updates with conditional CI runs triggered only when known UI changes occur. You can also utilize visual snapshots in isolated environments with mock data to reduce dynamic content noise.
For legacy tools without AI comparison capabilities, employ layered comparison approaches that start with pixel tolerance checking followed by semantic validation. Third-party libraries like ImageMagick can provide custom threshold configurations for older visual testing setups.
Solution Validation
After implementing each baseline update, re-run your visual tests to confirm no false positives appear. Use diff reports to verify that detected changes match actual UI modifications and no new regressions have been introduced. Monitor test flakiness reduction and baseline stability trends over several development cycles.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Implementation Challenges
| Issue | Symptoms | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Permission Errors | Cannot update baselines in repository | Check repository write permissions and CI/CD service account access |
| Wrong Baseline Version | Tests compare against outdated images | Verify baseline storage path and version tagging configuration |
| Dependency Conflicts | Image diff libraries fail to load | Update visual testing tool versions and resolve package conflicts |
| Inconsistent Screenshots | Same UI produces different images | Standardize browser versions, screen resolution, and rendering settings |
| False Positive Ignores | Dynamic content still triggers failures | Refine ignore region coordinates and expand coverage areas |
Edge Cases and Special Scenarios
Legacy applications with rapidly changing layouts require segmented baseline updates where different UI sections are managed independently. High-availability production environments need staged rollout of baseline updates to prevent widespread test failures during deployments.
Multi-tenant SaaS applications require tenant-specific baseline management since UI variations exist between different customer configurations. Scale challenges emerge when test suites and baseline repositories grow large, requiring periodic pruning and optimization to maintain performance.
When Solutions Don't Work
If baseline management issues persist, collect diagnostic logs and diff images to identify the exact source of mismatches. Validate that your rendering environment remains consistent across test runs, including browser versions, screen resolutions, and display settings.
Escalate persistent failures to your visual testing tool vendor with detailed reproduction steps and environment specifications. Consult community forums like Stack Overflow and GitHub Issues for similar cases, as other teams often share solutions for specific tool configurations.
Consider migrating to alternative visual testing platforms if current tools can't handle your baseline management requirements effectively.
Prevention Strategies
Long-term Prevention
Establish clear organizational policies where baseline updates only occur after proper review and approval of UI changes. Use ignore regions and AI-based comparisons consistently to minimize false positives from the start. Maintain all baselines under source control to track changes and enable rollback capabilities.
Educate your development, QA, and design teams about correct baseline management workflows. Everyone involved in UI changes should understand how their modifications affect visual testing and when baseline updates are necessary.
Optimization and Monitoring
Regularly prune and consolidate baseline images to keep repositories manageable as your application grows. Migrate to smarter AI-driven visual testing platforms when feasible, as they significantly reduce maintenance overhead compared to pixel-based approaches.
Integrate visual testing early in development cycles to catch UI drift before it becomes problematic. Automate baseline update approvals through gated pull request workflows that require both developer and QA sign-off.
Monitoring and Early Detection
| Metric | Alert Threshold | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Visual Test Failure Rate | Above 15% for 3 consecutive runs | Review recent UI changes and baseline accuracy |
| Baseline Update Frequency | More than 5 updates per week | Investigate if changes are intentional or process issues |
| Diff Severity Scores | High severity on critical user paths | Immediate investigation and potential rollback |
| Test Execution Time | 50% increase from baseline | Optimize test suite or baseline repository size |
Set up dashboards that monitor diff severity and show which UI components are most frequently affected by visual changes. This helps you identify areas that need more stable baseline management or better ignore region configuration.
Related Issues and Extended Solutions
Teams often encounter dynamic content rendering issues alongside baseline management problems. Mitigate these through comprehensive ignore zone configuration and mock data usage during visual testing. Environment drift between development, staging, and production can cause inconsistent screenshots, which standardized test environments address.
Integration challenges with CI/CD notification systems can delay defect identification and resolution. Configure your visual testing tools to integrate with Slack, Microsoft Teams, or email systems for immediate alerts when legitimate regressions are detected.
Advanced optimization techniques include implementing visual testing at the component level rather than full-page screenshots, which reduces baseline maintenance overhead and provides more granular change tracking. Performance improvements come from parallel test execution and optimized image storage solutions.
Bottom Line
Visual testing baseline management doesn't have to be a constant headache. Follow these steps: establish controlled baseline approval workflows, use AI-powered comparison methods, and maintain baselines under version control with proper ignore regions. Most teams see dramatic improvements within the first week of implementation.
The key is treating baseline management as a collaborative process between development, QA, and design teams rather than an automated CI/CD function. When everyone understands their role in maintaining visual test accuracy, false positives drop significantly and real regressions get caught faster.
Start with your most critical user journeys, get the baseline approval process working smoothly, then expand coverage. Takes about two to three days of initial setup, but you'll save hours every week once it's running properly. Your visual regression testing will finally do what it's supposed to do: catch real problems without the noise.




