Infrastructure Access Management: Securing Administrative Access Without Sacrificing Developer Productivity
Secure infrastructure administrative access without compromising developer productivity. Learn to implement role-based access controls, just-in-time access, and secure authentication methods. Discover strategies that maintain strong security posture while enabling efficient development workflows.
Introduction
Picture this scenario: It's 3 AM, your production environment is experiencing critical issues, and your on-call engineer needs immediate administrative access to resolve the problem. Traditional access management approaches would either leave permanent backdoors open for emergencies or create bureaucratic bottlenecks that delay resolution for hours. We've seen this dilemma play out countless times across organizations where infrastructure access management becomes a constant battle between security requirements and operational efficiency.
At VegaStack, we've helped dozens of companies navigate this challenge by implementing comprehensive infrastructure access management strategies that enhance security posture while preserving developer velocity. The key lies in adopting modern privileged access control mechanisms that provide granular oversight without creating productivity roadblocks.
This guide explores practical approaches to securing administrative access through just-in-time provisioning, comprehensive session monitoring, and robust audit trails. We'll walk through proven methodologies that satisfy compliance requirements while ensuring your teams can respond rapidly to operational demands.
The Infrastructure Access Management Challenge
The complexity of modern infrastructure access management stems from several converging factors that traditional security models struggle to address effectively. We recently worked with a mid-sized fintech company managing over 200 cloud instances across multiple environments, where their existing access controls were simultaneously too permissive and too restrictive.
Their development teams had standing administrative privileges across non-production environments, creating unnecessary attack surface exposure. Meanwhile, production access required manual approval processes that averaged 45 minutes during business hours and could extend to several hours during evenings and weekends. This approach resulted in both security vulnerabilities and operational delays that cost the organization approximately $8,000 monthly in extended incident resolution times.
Traditional privileged access approaches fail because they operate on binary permission models that don't reflect the nuanced reality of infrastructure operations. Static role assignments can't adapt to the dynamic nature of modern DevOps workflows, where access requirements fluctuate based on project phases, incident severity, and operational context. Additionally, conventional audit mechanisms often generate overwhelming log volumes without providing actionable insights into access patterns and potential security risks.
The technical complexities multiply when considering multi-cloud environments, containerized workloads, and ephemeral infrastructure components that challenge traditional identity and access management paradigms. Organizations need sophisticated frameworks that can seamlessly integrate with existing toolchains while providing comprehensive visibility into administrative activities.
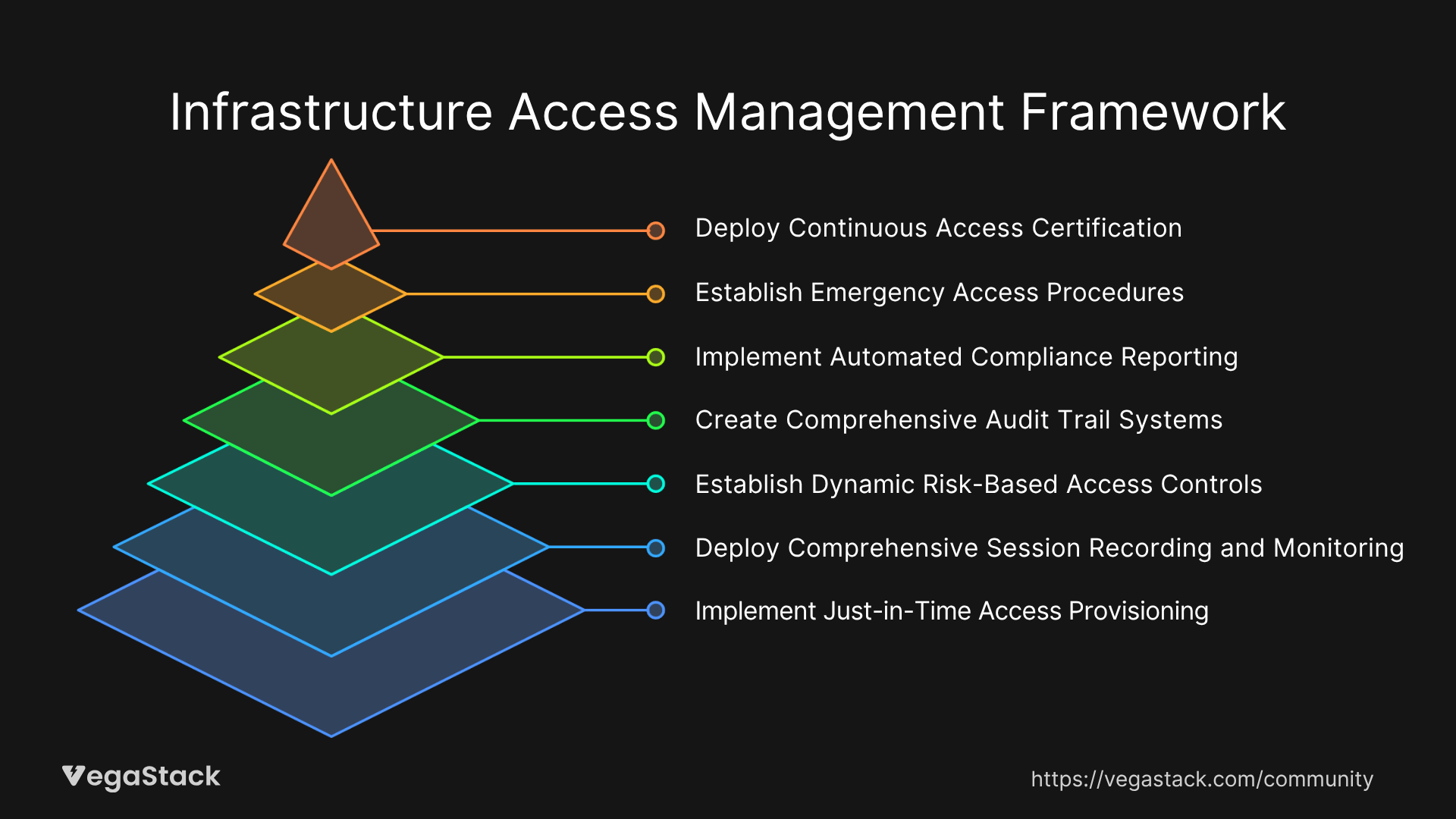
Comprehensive Infrastructure Access Management Framework
Step 1: Implement Just-in-Time Access Provisioning
Just-in-time access forms the cornerstone of modern infrastructure access management by eliminating standing privileges and providing temporary, purpose-specific access grants. We begin by cataloging all administrative access points across the infrastructure landscape, including cloud consoles, server SSH access, database administrative interfaces, and container orchestration platforms.
The implementation involves establishing automated workflows that can provision temporary credentials or elevate existing permissions based on predefined criteria. Access requests should include contextual information such as business justification, estimated duration, and specific resource scope. This approach reduces attack surface exposure by ensuring administrative privileges exist only when actively needed for legitimate purposes.
Step 2: Deploy Comprehensive Session Recording and Monitoring
Session recording capabilities provide crucial visibility into administrative activities while serving as both security controls and learning tools for incident post-mortems. We implement keystroke logging, screen recording, and command auditing across all administrative interfaces to create comprehensive activity records.
The monitoring system should capture not just what commands were executed, but also the context surrounding those actions, including timing, sequence, and environmental factors. This granular visibility enables security teams to identify unusual patterns, validate compliance with operational procedures, and reconstruct incident timelines with complete accuracy.
Step 3: Establish Dynamic Risk-Based Access Controls
Risk-based access controls adapt permission grants based on contextual factors such as user behavior patterns, access location, time of day, and current threat landscape. We configure systems to automatically adjust access requirements based on calculated risk scores that consider multiple variables simultaneously.
For example, access requests from familiar locations during business hours might require minimal approval, while requests from new locations or during unusual hours trigger additional verification steps. This dynamic approach balances security requirements with operational efficiency by applying appropriate controls based on actual risk levels.
Step 4: Create Comprehensive Audit Trail Systems
Effective audit trails extend beyond simple access logs to include correlation across multiple systems and enrichment with contextual metadata. We implement centralized logging that aggregates access events from all infrastructure components and correlates them with business processes, change management activities, and incident response actions.
The audit system should automatically flag anomalous patterns, such as unusual access times, privilege escalations, or access to sensitive resources outside normal operational patterns. These automated alerts enable proactive security monitoring while reducing the manual effort required for compliance reporting.
Step 5: Implement Automated Compliance Reporting
Automated compliance reporting transforms audit trail data into actionable insights that satisfy regulatory requirements while informing security policy improvements. We configure systems to generate regular reports that demonstrate adherence to access control policies, highlight trends in administrative activity, and identify potential areas for process optimization.
The reporting framework should support multiple compliance standards simultaneously, allowing organizations to demonstrate adherence to industry-specific requirements without maintaining separate audit systems for different regulatory frameworks.
Step 6: Establish Emergency Access Procedures
Emergency access procedures provide controlled mechanisms for bypassing normal approval workflows during critical incidents while maintaining security oversight and comprehensive logging. We implement break-glass access capabilities that grant immediate administrative privileges while triggering enhanced monitoring and automatic notifications to security teams.
These emergency procedures should include clear escalation paths, automatic time-based access revocation, and mandatory post-incident reviews to ensure emergency access capabilities aren't abused or overutilized.
Step 7: Deploy Continuous Access Certification
Continuous access certification processes regularly validate that administrative privileges remain appropriate for current business requirements and user responsibilities. We implement automated workflows that periodically review access grants, identify unused or excessive privileges, and prompt managers to certify ongoing access requirements.
This ongoing certification process prevents privilege creep and ensures access grants remain aligned with business needs as organizational structures and responsibilities evolve over time.
Implementation: Just-in-Time Access Architecture
The technical implementation of just-in-time access requires careful integration with existing identity providers, infrastructure automation tools, and monitoring systems. We typically deploy a centralized access broker that interfaces with multiple backend systems to orchestrate temporary privilege grants across diverse infrastructure components.
The access broker maintains an inventory of available resources, associated permission models, and integration capabilities with target systems. When processing access requests, the broker evaluates the request against established policies, initiates appropriate approval workflows, and coordinates credential provisioning across relevant systems. The broker also handles automatic access revocation based on time limits or explicit release actions.
Session recording integration presents unique technical challenges, particularly in containerized environments where traditional recording mechanisms may not capture all relevant activities. We implement recording capabilities at multiple layers, including container runtime integration, network traffic analysis, and application-specific audit logging to ensure comprehensive coverage across diverse infrastructure components.
The recording system must balance comprehensive coverage with storage efficiency and privacy considerations. We implement intelligent recording policies that adjust capture granularity based on the sensitivity of accessed resources and the risk profile of the requesting user. This approach minimizes storage requirements while ensuring critical activities receive appropriate monitoring coverage.
Results and Validation Metrics
Our infrastructure access management implementations typically demonstrate significant improvements across multiple security and operational metrics. A recent deployment with a healthcare technology company reduced their mean time to emergency access from 38 minutes to under 4 minutes, while simultaneously eliminating standing administrative privileges across 85% of their infrastructure.
The organization achieved a 73% reduction in excessive privilege assignments and improved their compliance audit preparation time by approximately 12 hours per quarter, translating to roughly $3,200 in saved consulting costs. Their security team reported 60% fewer false positive alerts due to improved contextual monitoring, allowing them to focus on genuine security concerns rather than routine administrative activities.
Session recording capabilities enabled the identification of several process inefficiencies that were costing the organization an estimated $1,800 monthly in extended incident resolution times. By analyzing recorded sessions, the team optimized their incident response procedures and identified opportunities for additional automation.
The audit trail enhancements satisfied their HIPAA compliance requirements while providing actionable insights that informed security policy improvements. The automated reporting capabilities reduced compliance documentation preparation time by 67%, while providing more comprehensive coverage than their previous manual processes.
However, we observed that initial implementation required careful change management to address user resistance to additional access controls. The transition period typically involves 4-6 weeks of elevated support requirements as teams adapt to new access patterns and emergency procedures.
Key Learnings and Best Practices
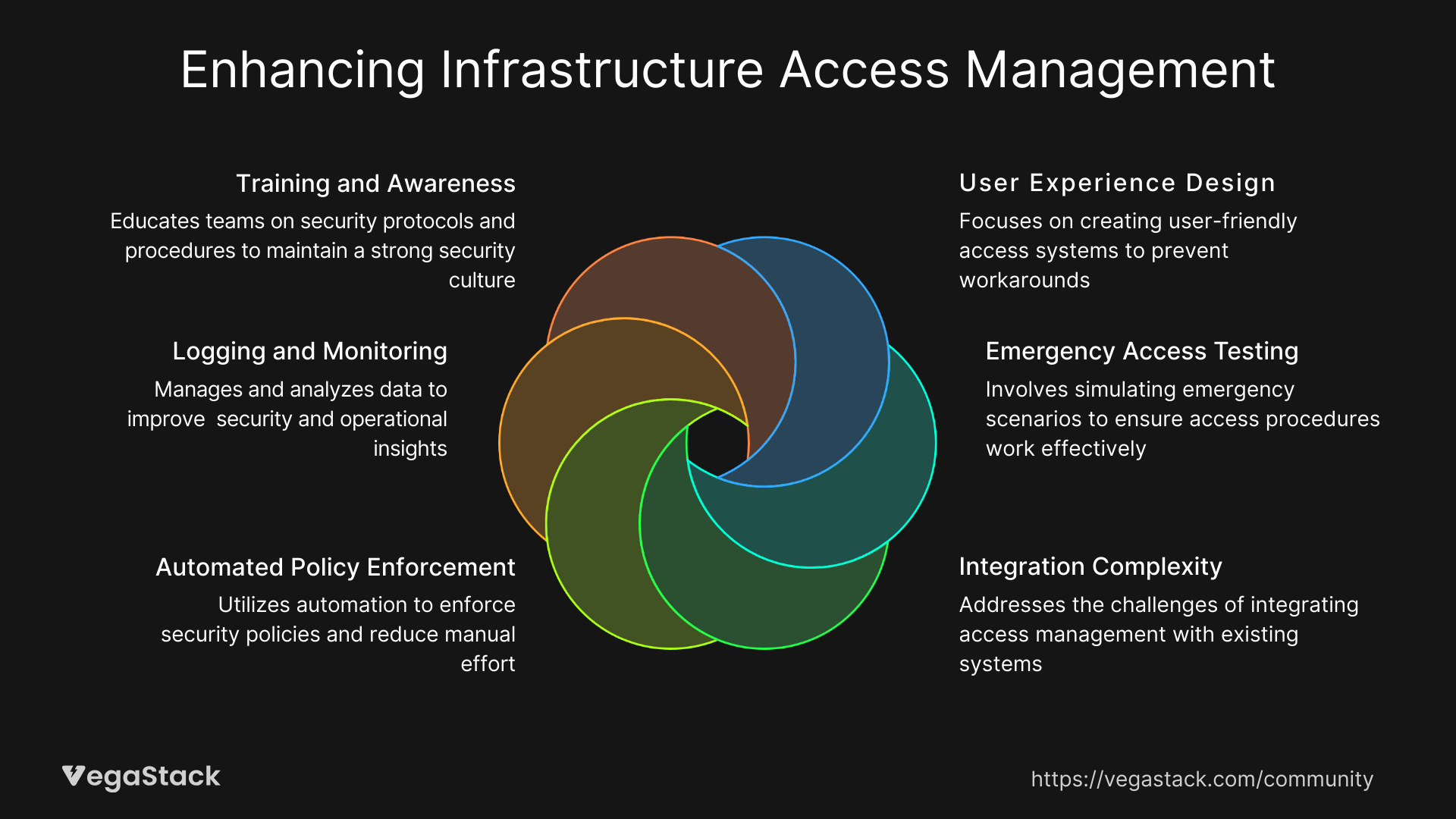
Through multiple infrastructure access management implementations, we've identified several fundamental principles that significantly impact success rates and user adoption. First, user experience design proves just as critical as security control effectiveness. Access management systems that create friction for legitimate activities inevitably face workaround attempts that undermine overall security posture.
Second, comprehensive testing of emergency access procedures under realistic conditions reveals gaps that aren't apparent during normal operations. We recommend regular tabletop exercises that simulate various incident scenarios to validate that emergency access capabilities actually work when needed most. These exercises often uncover dependencies and integration issues that could cause delays during actual emergencies.
Third, the integration complexity between access management systems and existing toolchains typically exceeds initial estimates. Organizations should plan for extended integration timelines and budget for custom development work to achieve seamless workflows across diverse infrastructure components.
Fourth, automated policy enforcement reduces both security risks and operational overhead compared to manual approval processes. However, the policy definitions require careful calibration to avoid either excessive restrictions or insufficient controls. We recommend starting with conservative policies and gradually relaxing restrictions based on operational experience and risk tolerance.
Fifth, comprehensive logging and monitoring generate substantial data volumes that require thoughtful storage and analysis strategies. Organizations should invest in log management capabilities that can handle the increased data volumes while providing responsive query and reporting capabilities.
Finally, ongoing training and awareness programs ensure that teams understand both the security rationale behind access controls and the proper procedures for requesting and using administrative privileges. Regular training updates help maintain security culture while addressing questions and concerns as they emerge.
Conclusion
Effective infrastructure access management requires balancing rigorous security controls with operational efficiency demands through comprehensive just-in-time access, session monitoring, and audit trail capabilities. The strategies outlined in this post provide proven frameworks for eliminating standing privileges while ensuring rapid response capabilities during critical incidents.
By implementing these infrastructure access management approaches, organizations can significantly enhance their security posture while actually improving operational efficiency through better visibility, automated workflows, and streamlined compliance processes. The key lies in treating access management as an enabler of secure operations rather than a barrier to productivity.




