Infrastructure Testing Strategies: Reduce Production Failures by 85% Before Deployment
Reduce production infrastructure failures by 85% with comprehensive testing strategies implemented before deployment. Learn automated testing approaches, chaos engineering principles, and validation techniques that catch issues early in the development lifecycle and ensure reliable deployments.

Introduction
We've all been there, that sinking feeling when a seemingly minor infrastructure change brings down production systems at 2 AM. Infrastructure testing has become the critical barrier between smooth deployments and career-defining outages. As infrastructure becomes increasingly complex with cloud-native architectures and microservices, the traditional "deploy and pray" approach simply doesn't scale.
At VegaStack, we've witnessed countless organizations struggle with infrastructure changes that work perfectly in development but wreak havoc in production. The challenge isn't just technical, it's cultural, requiring teams to shift from reactive troubleshooting to proactive validation. Through our experience helping enterprises implement robust production deployment validation processes, we've discovered that comprehensive testing strategies can reduce infrastructure-related incidents by up to 85%.
This guide explores the systematic approach we've developed for validating infrastructure changes before they reach production. We'll cover the three-tier testing framework that catches configuration errors early, the implementation challenges you'll face, and the measurable results you can expect. Whether you're managing traditional data centers or cloud-native environments, these strategies will transform how you approach infrastructure reliability.
The Critical Problem: Configuration Drift and Deployment Chaos
Infrastructure failures rarely announce themselves during development. We recently worked with a financial services client who experienced a cascading failure that cost them approximately $15,000 in downtime and emergency response. The culprit? A seemingly innocent load balancer configuration change that worked flawlessly in their staging environment but conflicted with production security policies.
This scenario illustrates the fundamental challenge of modern infrastructure management. Configuration drift between environments, dependency mismatches, and compliance violations create a minefield of potential failures. Traditional testing approaches focus heavily on application code while treating infrastructure as a secondary concern. This oversight becomes increasingly dangerous as infrastructure-as-code adoption grows and infrastructure changes become more frequent.
The complexity multiplies when considering cloud environments where infrastructure spans multiple services, regions, and providers. A single Terraform module might interact with dozens of cloud services, each with their own configuration requirements and constraints. Without systematic validation, teams operate blindly, discovering integration issues only after deployment.
What makes this problem particularly insidious is the delayed feedback loop. Unlike application bugs that often surface immediately, infrastructure issues can remain dormant until specific conditions trigger them. Network policies might work under normal load but fail during traffic spikes. Security configurations might function correctly until compliance audits reveal violations. This delayed discovery transforms minor configuration errors into major production incidents.
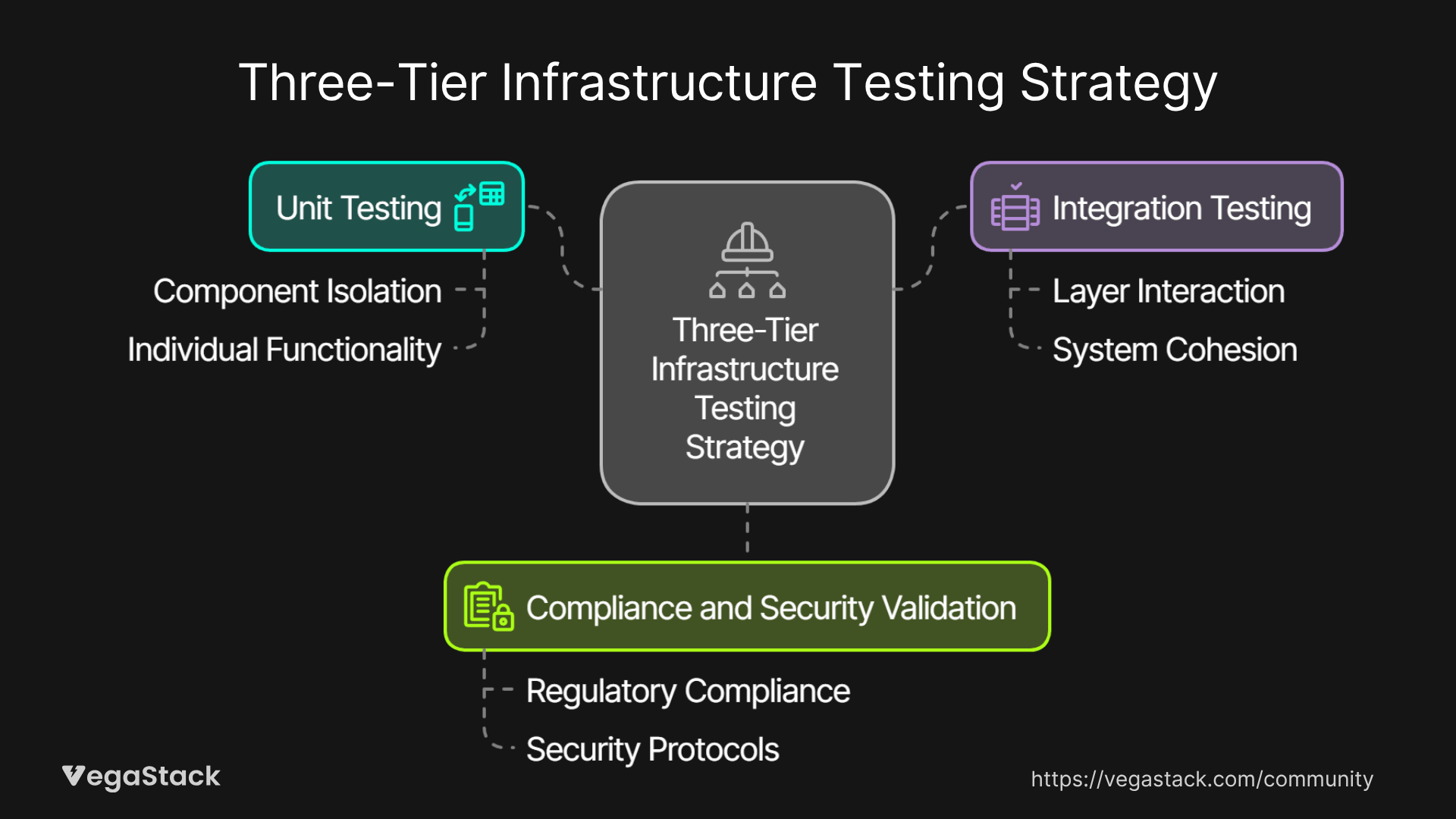
Solution Framework: Three-Tier Infrastructure Testing Strategy
Our comprehensive infrastructure testing approach consists of three interconnected validation layers that progressively increase in scope and complexity. Each tier serves a specific purpose while building upon the previous layer's foundation.
Tier One: Unit Testing for Infrastructure Components
The foundation begins with unit testing individual infrastructure components in isolation. This involves validating that each infrastructure module behaves correctly given specific inputs and constraints. We test resource creation logic, parameter validation, and dependency resolution without actually provisioning cloud resources.
Unit tests focus on the logical correctness of infrastructure definitions. They verify that security groups contain the expected rules, that IAM policies grant appropriate permissions, and that resource tags comply with organizational standards. This tier catches syntax errors, configuration inconsistencies, and policy violations before any cloud resources are created.
The key insight we've discovered is treating infrastructure modules like software libraries. Each module should have clearly defined interfaces, documented inputs and outputs, and comprehensive test coverage. This approach enables rapid feedback cycles and makes infrastructure changes more predictable and maintainable.
Tier Two: Integration Testing Across Infrastructure Layers
The second tier validates how infrastructure components interact with each other and with existing systems. Integration tests deploy infrastructure to isolated test environments and verify that all components work together as expected. This includes testing network connectivity, service discovery, data flow, and cross-service authentication.
Integration testing reveals issues that unit tests cannot detect – timing dependencies, resource limits, and environmental constraints. We deploy complete infrastructure stacks to dedicated test environments and run automated validation suites that verify every integration point. This includes testing failover scenarios, scaling behaviors, and recovery procedures.
One critical aspect we emphasize is testing infrastructure under realistic load conditions. Many configuration issues only surface when systems experience production-like traffic patterns or resource utilization. Integration tests should simulate these conditions to uncover potential bottlenecks and failure modes.
Tier Three: Compliance and Security Validation
The final tier focuses on organizational compliance, security policies, and regulatory requirements. This involves automated scanning for security vulnerabilities, policy compliance verification, and regulatory requirement validation. Compliance testing ensures that infrastructure changes don't introduce security risks or violate organizational standards.
We implement continuous compliance monitoring that evaluates infrastructure configurations against established baselines. This includes checking for exposed resources, validating encryption configurations, and ensuring that access controls follow the principle of least privilege. The goal is preventing compliance violations from reaching production environments.
Orchestrating the Testing Pipeline
The magic happens in orchestrating these three tiers into a cohesive validation pipeline. Each infrastructure change triggers the complete testing sequence, with failures at any tier preventing progression to the next stage. This creates multiple safety nets that catch different types of issues at appropriate stages in the deployment process.
Implementation: Automated Validation and Continuous Monitoring
The most challenging aspect of implementing comprehensive infrastructure testing is creating reliable automation that doesn't become a bottleneck. We've learned that successful implementation requires careful attention to test environment management and result interpretation.
Dynamic Test Environment Provisioning
Traditional approaches often struggle with test environment availability and consistency. We address this through dynamic provisioning of isolated test environments for each validation run. This ensures that tests run against clean, consistent infrastructure without interference from previous test runs or parallel executions.
The key innovation is treating test environments as transient resources that exist only for the duration of validation cycles. Each test run provisions a complete infrastructure stack, executes validation tests, collects results, and then destroys all resources. This approach eliminates environment drift and reduces testing costs while ensuring consistent results.
Intelligent Result Analysis and Reporting
Raw test results often overwhelm teams with information that's difficult to interpret and act upon. We've developed intelligent analysis systems that categorize failures by severity, provide actionable remediation suggestions, and track trends over time. This transforms testing from a compliance checkbox into a valuable feedback mechanism.
The reporting system correlates test results with infrastructure changes, helping teams understand which modifications introduced specific issues. This correlation accelerates debugging and helps teams learn from failures. We also implement automated notifications that alert relevant team members based on failure types and severity levels.
Progressive Deployment Validation
Beyond pre-deployment testing, we implement progressive validation during deployment processes. This involves deploying changes to subset environments, validating functionality, and gradually expanding scope based on validation results. This approach catches issues that only surface during actual deployment processes or under real-world conditions.
Results and Measurable Impact
Our clients typically see dramatic improvements in infrastructure reliability within the first quarter of implementation. One enterprise client reduced their infrastructure-related production incidents by 78% over 6 months, saving approximately $12,000 in incident response costs and prevented several potential major outages.
Quantitative Improvements
The testing framework delivers measurable improvements across multiple dimensions. Mean time to detection for infrastructure issues decreased from 45 minutes to under 8 minutes. Configuration error resolution time improved by 65% as teams received actionable feedback during development rather than after production deployment.
Deployment success rates increased from 73% to 94% for infrastructure changes, significantly reducing rollback requirements and emergency response scenarios. Teams reported 60% faster infrastructure development cycles as catching issues early eliminated lengthy debugging sessions and emergency fixes.
Qualitative Benefits
Beyond quantitative metrics, teams experience reduced stress and increased confidence in infrastructure changes. The systematic validation approach creates shared understanding of infrastructure behavior and promotes knowledge sharing across team members. Engineers report feeling more empowered to make infrastructure improvements knowing that comprehensive testing will catch potential issues.
The framework also improves collaboration between development and operations teams by providing common vocabulary and shared responsibility for infrastructure quality. This cultural shift proves as valuable as the technical improvements in many organizations.
Key Learnings and Best Practices
Through multiple implementations, we've identified several fundamental principles that determine success or failure of infrastructure testing initiatives.
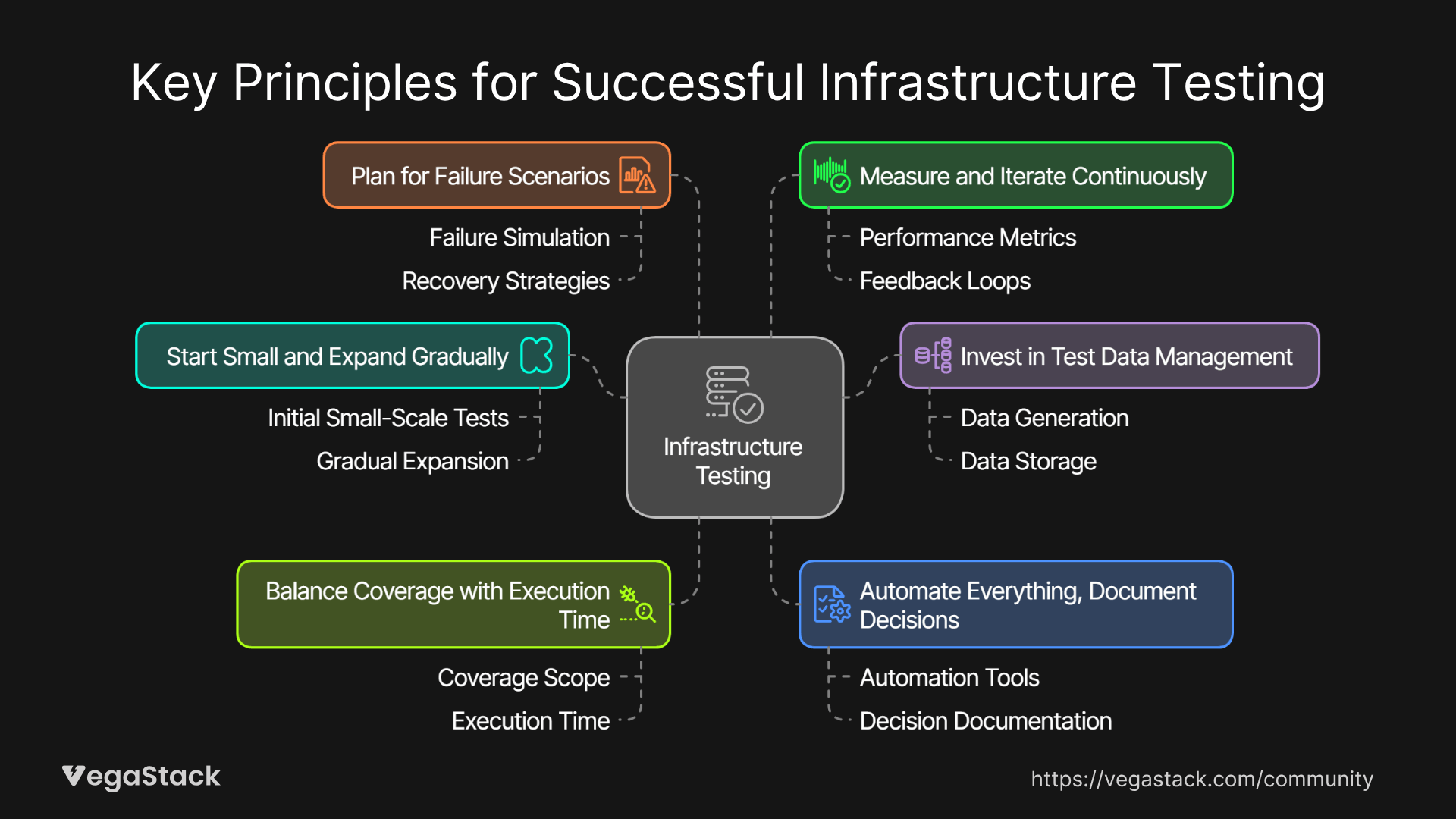
Start Small and Expand Gradually
The most successful implementations begin with a single, critical infrastructure component and gradually expand coverage. Attempting to implement comprehensive testing across entire infrastructure portfolios simultaneously often leads to overwhelm and abandonment. Focus on high-impact, frequently-changed components first to demonstrate value quickly.
Invest in Test Data Management
Infrastructure testing requires realistic test data that reflects production scenarios without exposing sensitive information. Develop strategies for generating synthetic data, anonymizing production datasets, and managing test data lifecycle. Poor test data undermines validation effectiveness and creates false confidence.
Balance Coverage with Execution Time
Comprehensive testing must remain fast enough to fit within development workflows. Teams abandon testing frameworks that significantly slow deployment cycles. Optimize test execution through parallelization, intelligent test selection, and efficient resource management. Aim for complete validation cycles under 15 minutes for typical infrastructure changes.
Automate Everything, Document Decisions
Manual testing steps inevitably become inconsistent and unreliable over time. Automate all validation processes while documenting the reasoning behind testing decisions. This documentation becomes invaluable for troubleshooting failures and onboarding new team members.
Plan for Failure Scenarios
Design testing frameworks with failure modes in mind. Consider what happens when test environments become unavailable, when cloud services experience outages, or when testing infrastructure itself needs updates. Robust error handling and graceful degradation prevent testing from becoming a single point of failure.
Measure and Iterate Continuously
Infrastructure testing strategies must evolve with infrastructure complexity and organizational needs. Implement metrics that track testing effectiveness, team satisfaction, and business impact. Use these insights to continuously refine testing approaches and expand coverage to new areas.
Conclusion
Infrastructure testing transforms from optional luxury to operational necessity as infrastructure complexity continues growing. The three-tier validation framework we've outlined are combining unit testing, integration validation, and compliance checking, provides comprehensive protection against configuration errors while maintaining development velocity.
The investment in systematic infrastructure validation pays dividends through reduced production incidents, faster development cycles, and increased team confidence. More importantly, it establishes the foundation for treating infrastructure with the same rigor and professionalism applied to application development.




