Introduction
Many companies face challenges with legacy infrastructure that restricts growth and hampers efficiency. Managing on-premises servers can be costly and inflexible, leading to missed opportunities and increased downtime.
Cloud migration offers a transformative solution, providing scalable, cost-effective, and secure alternatives. By moving to the cloud, companies can streamline operations, enhance performance, and unlock new potentials, positioning themselves for future success.
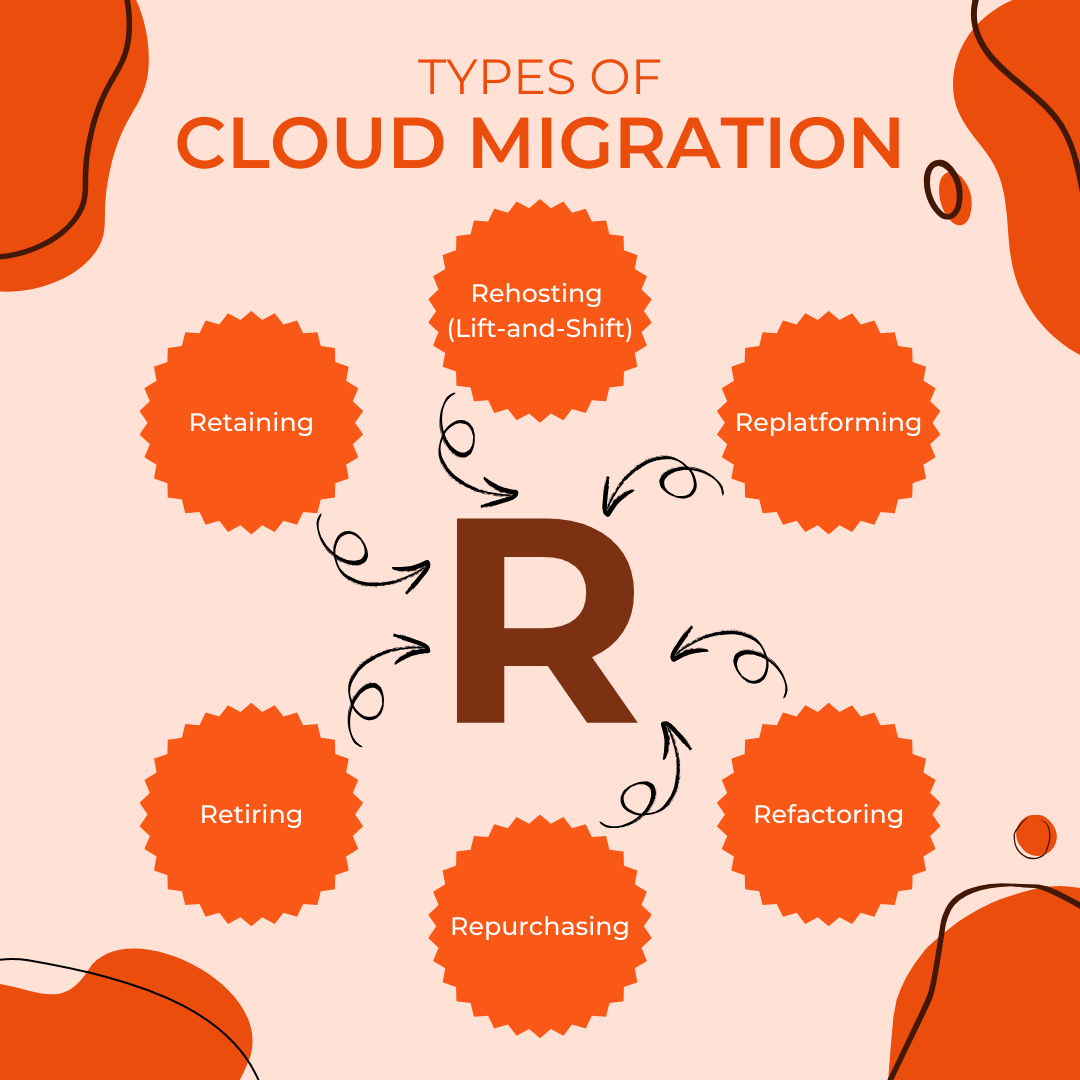
Types of Cloud Migration
Cloud migration is a strategic process that involves moving data, applications, and IT resources from on-premises systems to cloud-based platforms. There are several distinct approaches to cloud migration, each suited to different needs and goals. Understanding these types helps businesses choose the best strategy for their specific requirements.
- Rehosting (Lift-and-Shift): This method entails transferring applications and data to the cloud with few or no modifications. It’s often referred to as "lift-and-shift" because the primary goal is to relocate existing workloads quickly and cost-effectively. While this method can offer immediate benefits, such as reduced physical infrastructure costs, it may not fully leverage the advanced features of the cloud.
- Replatforming: Replatforming entails making some optimizations to applications while migrating them to the cloud. Unlike rehosting, this method involves modifying the application to take advantage of cloud-native features, such as managed databases or automated scaling. This can improve performance and efficiency without a complete overhaul of the application.
- Refactoring: Refactoring, or redesigning, involves re-architecting applications to fully utilize cloud capabilities. This approach often includes re-writing parts of the application to optimize it for cloud environments, enhancing scalability, performance, and resilience. While it requires more investment and time, it can lead to significant long-term benefits.
- Repurchasing: This approach entails replacing current applications with cloud-based solutions. It’s often referred to as "buying new" rather than migrating old systems. Repurchasing can streamline operations by leveraging advanced, purpose-built cloud solutions that offer better integration and functionality compared to legacy systems.
- Retiring: Retiring involves decommissioning outdated or unnecessary applications and services that are no longer needed. This approach helps reduce clutter and operational costs by eliminating redundant or obsolete systems, allowing organizations to focus on more valuable and strategic assets.
- Retaining: In some cases, businesses opt to keep certain applications on-premises while moving others to the cloud. This hybrid approach allows companies to gradually transition to the cloud, maintaining critical legacy systems while taking advantage of cloud benefits for new or less critical applications.
Benefits of Cloud Migration
Migrating to the cloud offers a multitude of advantages that can significantly enhance business operations and drive growth. Here are several key advantages of embracing cloud technology:
- Cost Efficiency: Cloud migration often leads to substantial cost savings by reducing the need for physical hardware and associated maintenance. Organizations pay only for the resources they use, which can lower capital expenditures and operational costs. Additionally, the cloud’s pay-as-you-go model allows businesses to scale resources up or down based on demand, optimizing costs and eliminating waste.
- Scalability and Flexibility: The cloud provides unparalleled scalability, allowing businesses to adjust their IT resources in real-time according to their needs. This flexibility means companies can handle varying workloads and adapt to market changes without the constraints of physical infrastructure. Whether expanding operations or launching new projects, the cloud’s adaptable nature supports rapid growth and innovation.
- Improved Performance: Cloud services often offer superior performance through advanced infrastructure and optimized resources. With access to the latest technologies and high-performance computing capabilities, businesses can experience faster processing speeds, reduced latency, and enhanced application responsiveness. This performance boost can lead to better user experiences and increased productivity.
- Enhanced Security: Leading cloud providers implement robust security measures, including encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular security updates. These advanced security protocols help protect sensitive data from cyber threats and breaches. Additionally, cloud environments often benefit from continuous monitoring and compliance with industry standards, providing a higher level of security compared to many on-premises systems.
- Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity: The cloud offers effective disaster recovery solutions, ensuring that data is backed up and easily recoverable in case of unforeseen events. Cloud-based systems are designed for high availability and redundancy, minimizing downtime and ensuring business continuity. This resilience helps organizations quickly bounce back from disruptions and maintain operations.
- Access to Latest Technologies: Cloud migration grants businesses access to cutting-edge technologies, such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and big data analytics. By leveraging these advanced tools, companies can drive innovation, improve decision-making, and stay competitive in a rapidly evolving market.
Challenges of Cloud Migration
While cloud migration offers numerous benefits, it also presents several challenges that organizations must navigate to ensure a successful transition. Recognizing these challenges enables businesses to better prepare and address potential obstacles:
- Initial Costs and Complexity: While cloud migration can result in long-term savings, the initial expenses and complexity can be considerable. Expenses may cover cloud service fees, consulting charges, and migration tools. Additionally, the complexity of planning and executing a migration can be daunting, requiring detailed assessments, strategic planning, and coordination across teams. Proper budgeting and project management are essential to address these complexities effectively.
- Data Security and Compliance: Ensuring data security and meeting compliance requirements are critical concerns during cloud migration. Organizations must carefully evaluate the security measures provided by cloud vendors and ensure they align with industry regulations and standards. Managing sensitive data and maintaining compliance with laws such as GDPR or HIPAA can be challenging, requiring robust security protocols and continuous monitoring.
- Downtime and Disruption Risks: Migrating to the cloud can lead to temporary disruptions or downtime, affecting business operations. Careful planning and phased migration strategies can help minimize these risks, but organizations should be prepared for potential impacts on productivity. Implementing thorough testing and validation processes can help ensure a smooth transition with minimal operational interruptions.
- Vendor Lock-In: Cloud migration may result in vendor lock-in, where businesses become dependent on a specific cloud provider's services and tools. This can limit flexibility and make it challenging to switch providers or adopt new technologies. To mitigate this risk, organizations should consider using open standards and multi-cloud strategies, which can provide greater flexibility and reduce dependency on a single vendor.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Connecting cloud services to existing legacy systems can be intricate and require significant time and effort. Ensuring compatibility and seamless operation between new cloud-based solutions and on-premises systems requires careful planning and technical expertise. Addressing integration challenges early in the migration process can help avoid disruptions and ensure a more cohesive IT environment.
Best Practices for Cloud Migration
Successful cloud migration requires careful planning and execution. By following best practices, organizations can ensure a smooth transition and maximize the benefits of their new cloud environment. Consider these essential best practices:
- Assessment and Planning: Start by conducting a comprehensive assessment of your current IT infrastructure, applications, and business needs. Develop a thorough migration strategy that outlines objectives, schedules, and required resources. This planning phase should involve stakeholders from across the organization to ensure alignment and address potential challenges early on.
- Choosing the Right Cloud Model: Evaluate different cloud models—Public, Private, and Hybrid—to determine which best suits your business needs. Public clouds offer scalability and cost-effectiveness, Private clouds provide enhanced security and control, and Hybrid clouds offer a balanced approach, combining the benefits of both. Choose a model that aligns with your organization's goals and compliance requirements.
- Data Migration Strategies: Implement effective data migration strategies to ensure the integrity and security of your data. Use migration tools and services that can handle large volumes of data and minimize downtime. Ensure data quality by validating and cleaning data prior to migration. Adopt a phased strategy to migrate data in stages, minimizing risk and enabling testing and adjustments.
- Testing and Validation: Thoroughly test and validate applications and systems before and after migration. Conduct performance testing to ensure that cloud resources meet your needs and that applications function correctly in the new environment. Address any issues identified during testing to ensure a smooth and reliable transition.
- Training and Support: Provide training for your team to familiarize them with new cloud tools and processes. Effective training helps ensure that staff can efficiently manage and utilize the cloud environment. Additionally, establish support mechanisms, such as dedicated helpdesks or vendor support services, to address any issues that arise post-migration.
Future Trends in Cloud Migration
As technology evolves, cloud migration continues to adapt, incorporating new trends and innovations that enhance its capabilities and benefits. Here are some key future trends shaping the landscape of cloud migration:
- AI and Machine Learning Integration: The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) into cloud environments is becoming increasingly prevalent. These technologies enable advanced data analytics, predictive insights, and automation, improving decision-making and operational efficiency. AI-driven tools can optimize cloud resource management, enhance security through anomaly detection, and personalize user experiences, driving innovation and competitive advantage.
- Serverless Computing: Serverless computing is gaining traction as an efficient way to manage cloud resources. Serverless architecture allows developers to create and deploy applications without the need to manage the underlying servers. This model allows for automatic scaling, reduced operational overhead, and cost savings by charging only for actual usage. Serverless computing simplifies application development and accelerates delivery to market.
- Edge Computing: As the demand for real-time data processing grows, edge computing is emerging as a critical trend. Edge computing processes data near its source, like IoT devices, to minimize latency and optimize bandwidth usage. This approach enhances the performance of applications that require immediate data analysis and response, such as autonomous vehicles and smart cities, while complementing cloud resources.
- Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Cloud Strategies: The use of multi-cloud and hybrid cloud strategies is growing steadily. Multi-cloud involves using services from multiple cloud providers to avoid vendor lock-in and enhance redundancy, while hybrid cloud combines private and public clouds to balance security, flexibility, and cost. These strategies offer greater flexibility, risk management, and optimized resource allocation, enabling organizations to tailor their cloud environments to specific needs.
As these trends continue to evolve, they will further shape the future of cloud migration, offering new opportunities for businesses to innovate and optimize their IT strategies. Embracing these trends can help organizations stay ahead of the curve and fully leverage the potential of cloud technologies.
Key Takeaways
- Diverse Migration Approaches: Rehosting, replatforming, refactoring, repurchasing, retiring, and retaining each offer different benefits and considerations for cloud migration.
- Cost Efficiency: Cloud migration can reduce physical infrastructure costs and optimize resource spending with a pay-as-you-go model.
- Enhanced Performance and Scalability: Cloud solutions provide improved performance and flexibility, allowing for better resource management and faster scaling.
- Security and Compliance: Cloud providers offer advanced security features, but businesses must ensure these meet their specific compliance and security needs.
- Emerging Trends: AI, serverless computing, edge computing, and multi-cloud strategies are shaping the future of cloud migration, offering new opportunities for innovation and efficiency.
Conclusion
Cloud migration offers significant benefits like cost efficiency, scalability, and improved performance, along with enhanced security and disaster recovery. Despite these advantages, businesses must navigate challenges such as initial costs, data security, and integration issues.
Choosing the right migration approach—whether rehosting, replatforming, or refactoring—is crucial. Additionally, staying abreast of trends like AI, serverless computing, and multi-cloud strategies can further optimize cloud adoption. With careful planning and execution, organizations can leverage the cloud to drive innovation and stay competitive.

