Choose a different version or distribution
Introduction
Before we begin talking about how to install and configure Monit on Ubuntu 18.04, let’s briefly understand – What is Monit?
Monit is a program that helps to manage as well as monitor the server programs automatically not only to stay online constantly, but also the size of the file, and permission are always correct. Moreover, Monit comes along with and web interface that helps to set the processes easily.
It can be used to monitor processes, files, directories, and network services, ensuring their availability and responsiveness. Setting up and configuring Monit is relatively straightforward.
This tutorial will walk you through the steps required to install and configure Monit on your Linux system. We will also address a few FAQs on how to install and configure Monit on Ubuntu 18.04.
Advantages to Install and Configure Monit
- Proactive Monitoring: Monit provides real-time monitoring, enabling proactive detection of issues, allowing for immediate corrective actions before they impact the system's performance and availability.
2. Automatic Service Restarts: Monit can automatically restart failed services, ensuring continuous operation and minimizing downtime.
3. Flexible Configuration: With Monit's configuration file, you have granular control over the monitoring parameters, thresholds, and actions, allowing for customization based on your specific monitoring needs.
4. Notifications and Alerts: Monit sends email notifications about critical events or issues, providing timely alerts to system administrators for prompt investigation and resolution.
5. Web Interface: Monit offers a web interface that provides a centralized view of the system's status, facilitating easy monitoring, administration, and configuration updates from any web browser.
Step 1 - Installing Monit
1) It is very easy to install Monit using apt-get.
sudo apt-get install monit
2) After installing, add the programs, and processes to the configuration file using the following command:
sudo nano /etc/monit/monitrc
There is already configuration for enabling web interface, but it is commented by default. You can comment out the following lines already present in monitrc file. You can change by default username and password for security reasons.
set httpd port 2812
allow admin:monit # require user 'admin' with password 'monit'
3) Using the command, it will start the Monit and let it run in the background.
monit
4) After that, type monit status to get Monit details.
The Monit daemon 5.3.2 uptime: 1h 25m
System 'myhost.mydomain.tld'
status Running
monitoring status Monitored
load average [0.03] [0.14] [0.20]
cpu 3.5%us 5.9%sy 0.0%wa
memory usage 26100 kB [10.4%]
swap usage 0 kB [0.0%]
data collected Thu, 30 Aug 2012 18:35:00
Step 2 - Configuring Monit
Monit is mainly easy to use, as it is set by default to check those services that are running in every 2 minutes, and store its log file in “/var/log/monit.log”.
These files will further get alter at the beginning of the configuration in both set daemon and set logfile lines.
Web Service
Monit usually comes with its own server that runs on Port 2812.
1) Now, to configure the web interface, search and then uncomment the section that starts with the set httpd port 2812. After it is done, write in the server’s IP, or the domain name as the address, allowing access to anyone to connect. After that, create Monit user as well as the password.
set httpd port 2812
use address 12.34.56.789 # only accept connection from localhost
allow 0.0.0.0/0.0.0.0 # allow localhost to connect to the server and
allow admin:monit # require user 'admin' with password 'monit'
2) After the configuration is done, Monit will reload and then re-read the file of configuration, therefore, web interface will be available.
monit reload
3) After that, you will be able to access the Monit web interface, by going to "example.com:2812".
4) Login with the chosen user-name and password. Your screen will look like this:
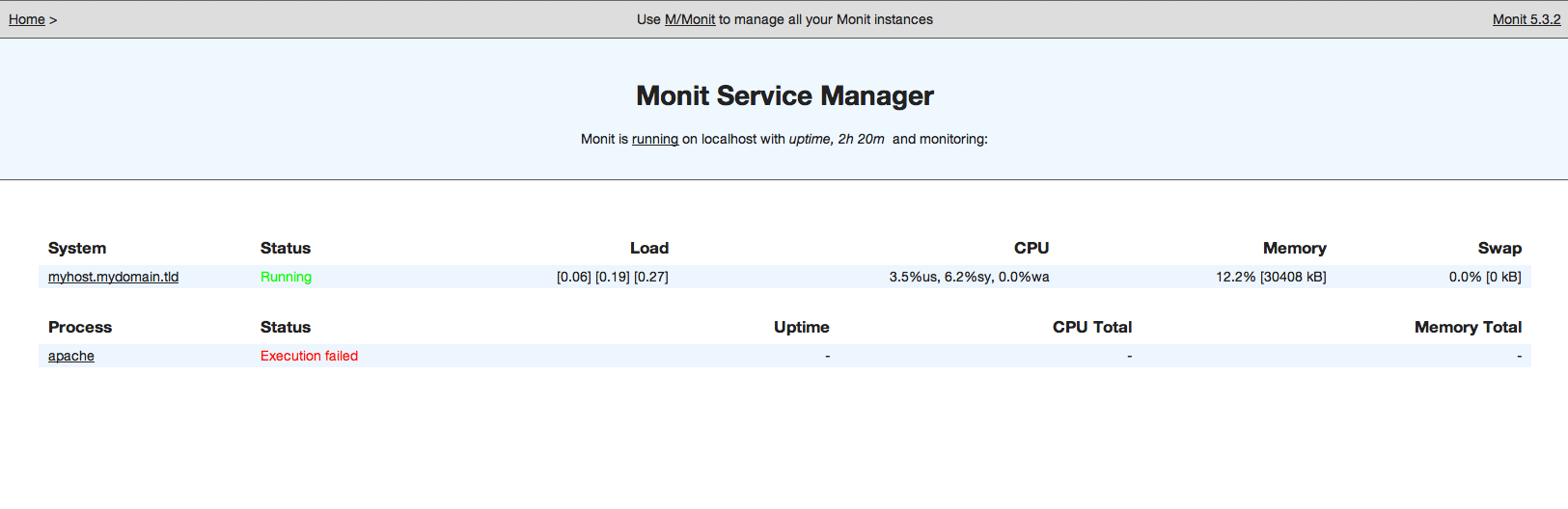
Step 3 - Configuring Programs Self-Monitoring
1) Further, once the services of the web are set up, you can now proceed to enter the programs that need monitoring and protecting /etc/monit/monitrc into the configuration file.
2) After that, use the /etc/init.d command to ensure that the programs stay online and to start or stop the program.
Some Configuration Examples are as follows:
Apache:
check process apache with pidfile /run/apache2.pid
start program = "/etc/init.d/apache2 start" with timeout 60 seconds
stop program = "/etc/init.d/apache2 stop"
MySQL:
check process mysqld with pidfile /var/run/mysqld/mysqld.pid
start program = "/etc/init.d/mysql start"
stop program = "/etc/init.d/mysql stop"
Nginx:
check process nginx with pidfile /var/run/nginx.pid
start program = "/etc/init.d/nginx start"
stop program = "/etc/init.d/nginx stop"
After all the programs are configured that you wish to run, they will automatically track and restart. You will be able to control the programs using a web interface or the command line.
3) After setting the configuration, check the syntax using the following command:
monit -t
4) Remove any syntax error in the program, then run it again.
monit start all
set httpd port 2812
FAQs to Install and Configure Monit on Ubuntu 18.04
How do I install Monit on my Linux system?
You can install Monit using the package manager of your Linux distribution. For example, on Ubuntu, you can use the command sudo apt-get install monit.
What are the basic configuration steps for Monit?
After installing Monit, you need to modify the configuration file, usually located at /etc/monitrc. You can define the services you want to monitor, set up email notifications, configure intervals for checks, and enable the Monit web interface.
What services can Monit monitor?
Monit can monitor various services, including processes, files, directories, network services (such as HTTP, FTP, SMTP), system resources (CPU, memory), and more.
How can I monitor a specific process with Monit?
To monitor a process, you define a service block in the Monit configuration file, specifying the process name or ID, check interval, start and stop command, and other relevant parameters.
How do I start and stop Monit?
You can start and stop the Monit service using the appropriate commands for your Linux distribution. For example, on Ubuntu, you can use sudo service monit start and sudo service monit stop.
How secure is the Monit web interface?
The Monit web interface can be secured by configuring HTTPS, username/password authentication, and restricting access to specific IP addresses.
How can I monitor system resources like CPU and memory with Monit?
Monit can monitor system resources by defining resource checks in the Monit configuration file, specifying thresholds for CPU usage, memory usage, and other system resource parameters.
Conclusion
Installing and configuring Monit on your Linux system provides you with a powerful monitoring and management tool. By effectively setting up Monit, you gain the ability to monitor processes, files, directories, and network services, ensuring their availability and responsiveness.
With features like automatic service restarts, email notifications, and the web interface, Monit allows for proactive monitoring and quick response to any issues or failures. By following the installation steps and configuring the Monit configuration file as mentioned in the tutorial, you can tailor the tool to meet your specific monitoring requirements.
If you have any queries, please leave a comment below, and we’ll be happy to respond to them for sure.

