Choose a different version or distribution
Introduction
Before we begin talking about how to install Laravel on Ubuntu 24.04, let's briefly understand – What is Laravel?
Laravel is a popular open-source PHP framework known for its elegant syntax and robust features, facilitating rapid web application development.
With built-in tools like Eloquent ORM and Blade templating engine, Laravel simplifies tasks such as database management and template rendering. Its scalability, intuitive syntax, and extensive community support make it a top choice for building dynamic and secure web applications efficiently.
In this tutorial, you will install Laravel on Ubuntu 24.04. We will also address a few FAQs on how to install Laravel on Ubuntu 24.04.
Advantages of Laravel
- Elegant Syntax: Laravel boasts clean and expressive syntax for streamlined coding.
- Modularity: Offers modular packaging system with Composer for easy component integration.
- ORM Support: Eloquent ORM simplifies database interactions and management tasks.
- Security Features: Built-in security features like hashed and salted passwords enhance application security.
- Community Support: Active Laravel community provides resources, packages, and constant updates for developers.
Prerequisites
Before diving into this guide, ensure you have the following prerequisites:
- An Ubuntu 24.04 server.
- A non-root user with administrative privileges.
Installing LAMP Stack and Composer
Laravel is a widely-used PHP web framework for contemporary web development. To get started, make sure PHP and other required dependencies are installed on your Ubuntu server. In this section, you'll install Laravel using the LAMP Stack (Linux, Apache, MySQL/MariaDB, and PHP) along with Composer.
Before proceeding with the installation, execute the following command to update your Ubuntu repository.
sudo apt update
Next, execute the following command to install Laravel's dependencies, which include the LAMP Stack (Linux, Apache, MySQL/MariaDB, and PHP), Composer, and Git.
sudo apt install apache2 mariadb-server php php-curl php-bcmath php-json php-mysql php-mbstring php-xml php-tokenizer php-zip composer git
Press Y to continue with the installation.
After the installation is complete, verify the status of both the Apache and MariaDB services, as well as the versions of PHP and Composer.
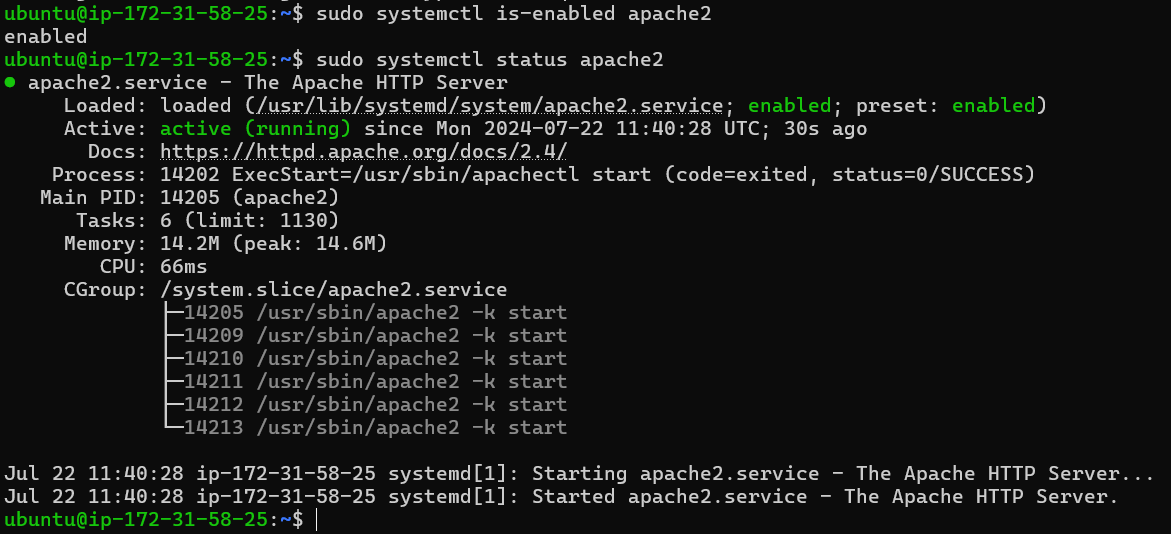
Use the following command to check the Apache service status. By default, the Apache service on Ubuntu should be enabled and running automatically.
sudo systemctl is-enabled apache2
sudo systemctl status apache2
Output:
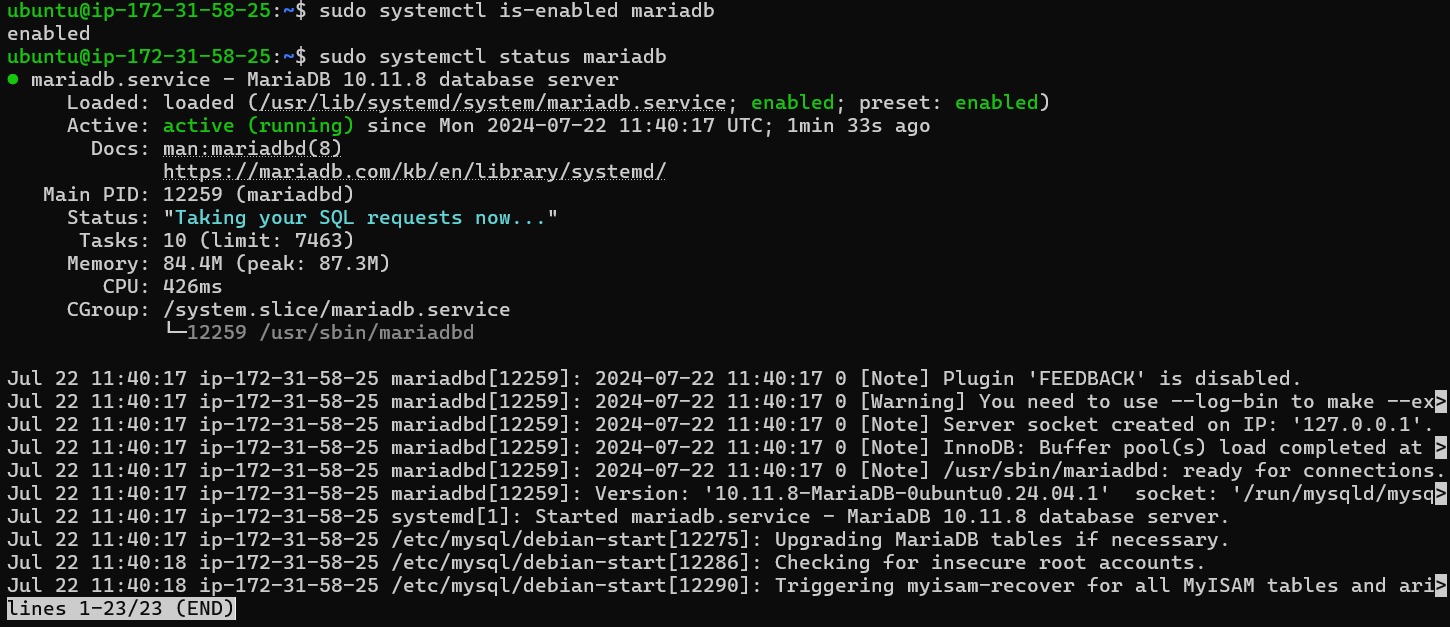
Next, use the command below to check the MariaDB service. The MariaDB server should be enabled and running on your Ubuntu system.
sudo systemctl is-enabled mariadb
sudo systemctl status mariadb
Output:
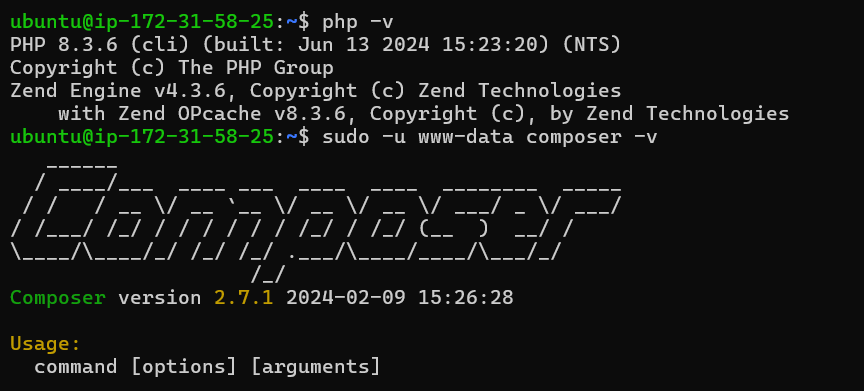
Finally, use the command below to check the versions of PHP and Composer. You should see PHP 8.3 and Composer 2.7.1 installed on your system.
php -v
sudo -u www-data composer -v
Optional: Installing Node.js and NPM (Node.js Package Manager)
Node.js and NPM are necessary if you're using Laravel with a templating engine like Blade or incorporating JavaScript. In this section, you'll install both Node.js and NPM (Node.js Package Manager) from the Ubuntu repository.
To do so, run the following commands on your Ubuntu system:
sudo apt install nodejs npm
Type Y to confirm the installation.
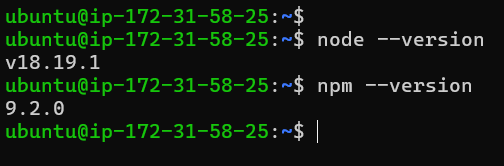
Once the installation is complete, use the command below to check the versions of Node.js and NPM.
node --version
npm --version
The output below indicates that Node.js 18 and NPM 9.5 are installed.
Configuring PHP
To run Laravel, you need to ensure that certain PHP extensions, such as fileinfo, mbstring, and openssl, are enabled. To enable these extensions, you'll need to modify the php.ini file.
Use the nano editor to edit the default PHP configuration file located at /etc/php/8.3/apache2/php.ini.
sudo nano /etc/php/8.3/apache2/php.ini
Uncomment the lines below to enable the PHP extensions fileinfo, mbstring, and openssl.
extension=fileinfo
extension=mbstring
extension=openssl
Save the file and exit the editor.
Then, run the command below to restart the Apache service and apply the PHP changes.
sudo systemctl restart apache2
Next, verify that the PHP extensions fileinfo, mbstring, and openssl are enabled by running the following command. If the extensions are active, their names will be displayed.
sudo php -m | grep 'fileinfo\|mbstring\|openssl'
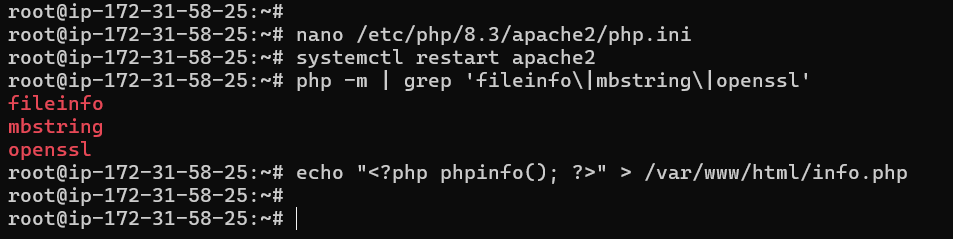
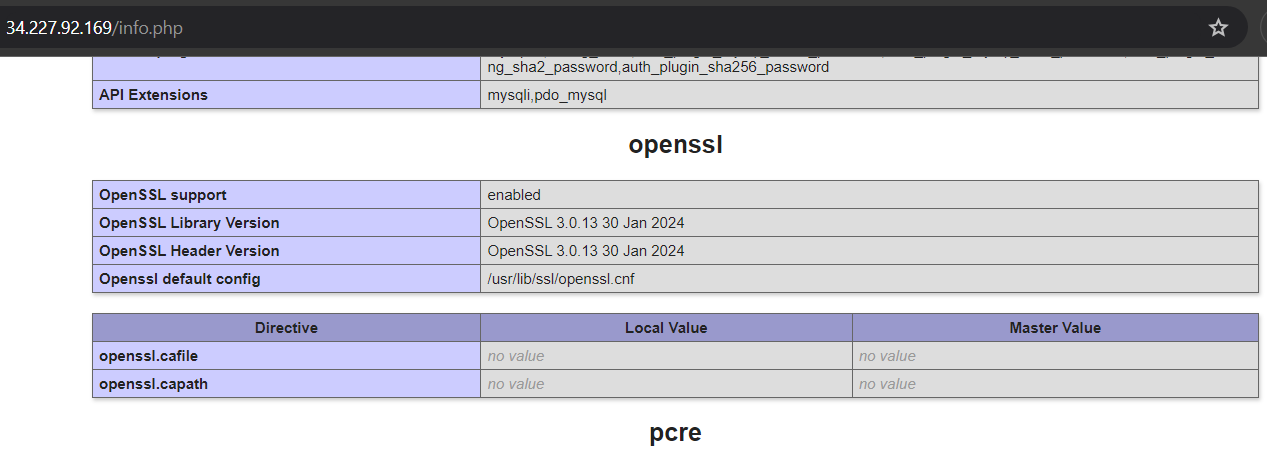
Additionally, you can check the list of enabled PHP extensions using PHPINFO. Create a new PHPINFO file with the following command.
echo "<?php phpinfo(); ?>" > /var/www/html/info.php
Next, go to http://YOUR_IP/info.php. Verify that the extensions fileinfo, mbstring, and openssl are listed to ensure they are enabled.
Configuring MariaDB server
After configuring PHP, you should secure your MariaDB server and create a new database and user for Laravel.
Run the mariadb-secure-installation command to secure your MariaDB server. You will then be prompted to configure the MariaDB server settings.
sudo mariadb-secure-installation
When prompted, enter Y to apply the new configuration or N to reject it.
- The default MariaDB installation does not have a password; press ENTER when asked for the password.
- Then, input
Yto set a root password for MariaDB, type and confirm the new password. - Input
Yto remove the anonymous user,Yagain to disable remote login for the root user, andYto delete the default test database. - Finally, input
Yto reload table privileges and apply the changes.
After securing the MariaDB server, you'll need to create a new database and user for your Laravel project.
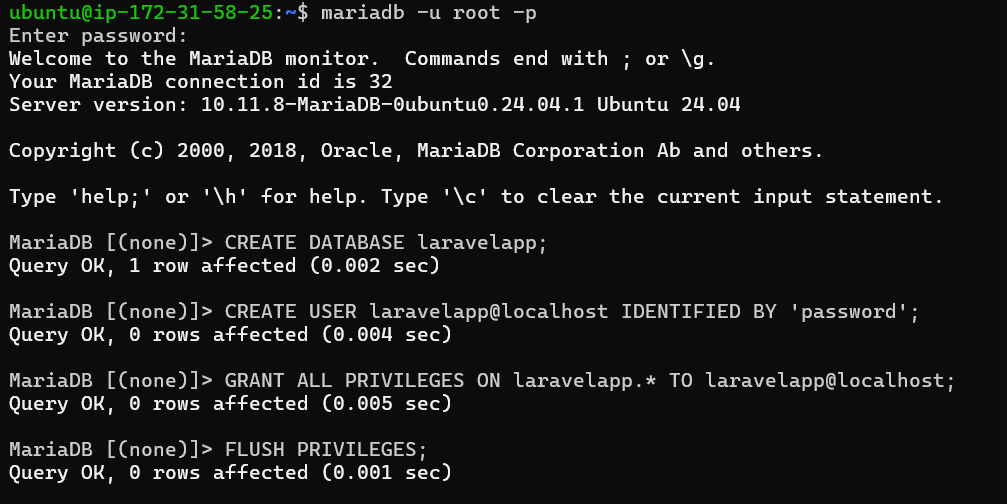
Log in to the MariaDB server using the command below and enter your MariaDB root password when prompted.
sudo mariadb -u root -p
Next, execute the following queries to create a new database and a user named laravelapp with the password password.
CREATE DATABASE laravelapp;
CREATE USER laravelapp@localhost IDENTIFIED BY 'password';
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON laravelapp.* TO laravelapp@localhost;
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
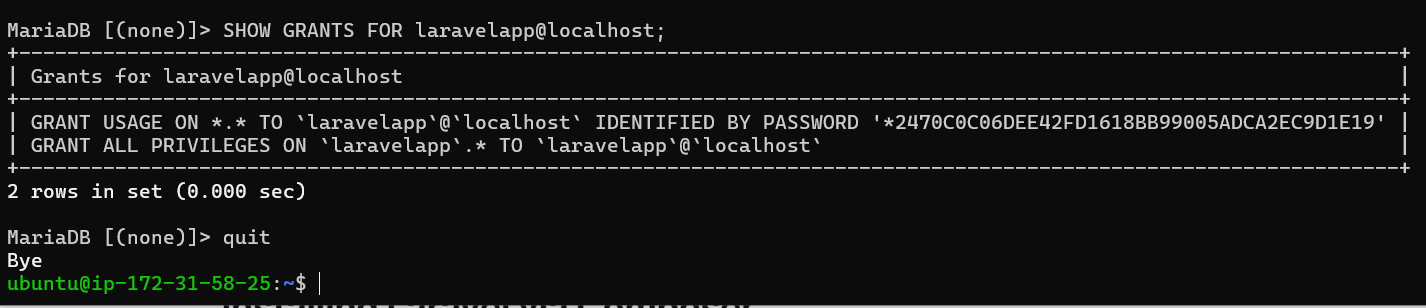
Next, execute the following query to verify the privileges for the user laravelapp. This will confirm that the user has access to the Laravel database laravelapp.
SHOW GRANTS FOR laravelapp@localhost;
Lastly, type quit to exit from the MariaDB server.
Installing Laravel via Composer
With PHP configured and the MySQL/MariaDB database and user created, you're ready to install Laravel. In this section, you'll set up the project directory, install Laravel using Composer, and connect Laravel to the MySQL/MariaDB database.
First, run the command below to create the directories /var/www/.cache (for Composer cache), /var/www/.config (for additional Composer configuration), and /var/www/laravelapp (for your Laravel project).
sudo mkdir -p /var/www/{.cache,.config,laravelapp}
Next, change the ownership of the /var/www/.cache, /var/www/.config, and /var/www/laravelapp directories to the www-data user.
sudo chown -R www-data:www-data /var/www/{.cache,.config,laravelapp}
Then, navigate to the /var/www/laravelapp directory and install Laravel using the Composer command below.
cd /var/www/laravelapp/
sudo -u www-data composer create-project laravel/laravel .
The Laravel installation process should start as follows:
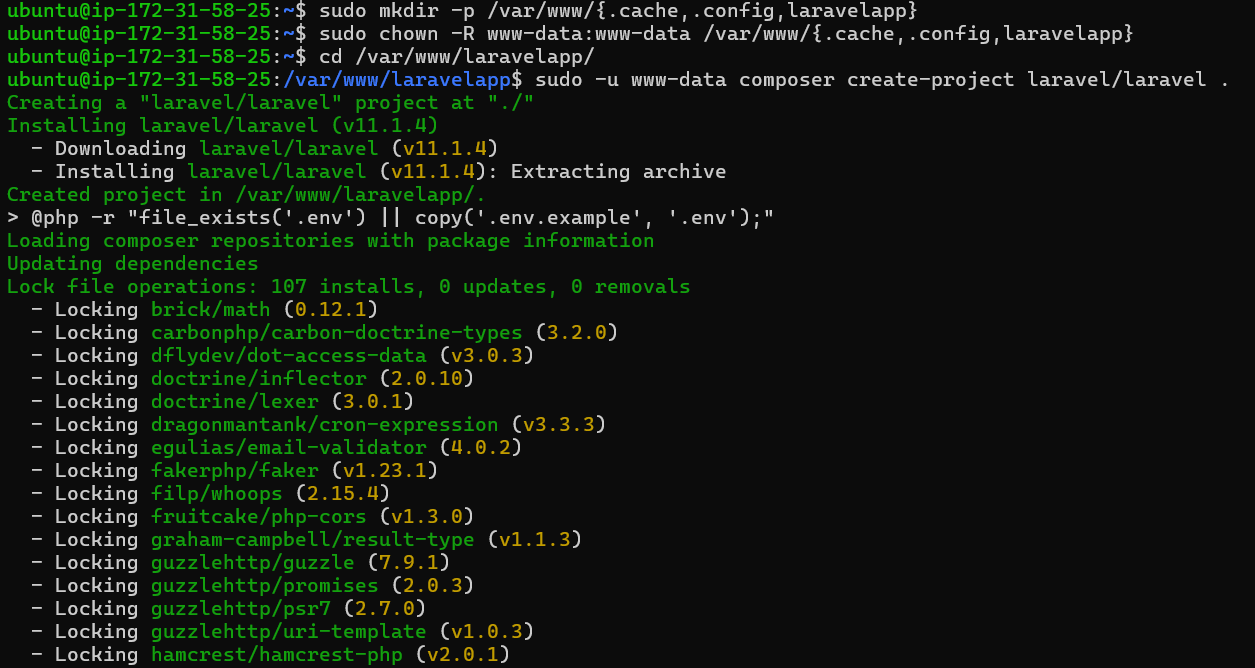
Now, open the .env file using the nano editor with the command below.
nano .env
Update the default APP_URL with your local domain name. In this example, Laravel will be configured to run on the domain laravelapp.local.
APP_URL=http://laravelapp.local
Set the DB_CONNECTION to mysql, then uncomment and update the database details with your own information.
DB_CONNECTION=mysql
DB_HOST=127.0.0.1
DB_PORT=3306
DB_DATABASE=laravelapp
DB_USERNAME=laravelapp
DB_PASSWORD=password
Save and close the file.
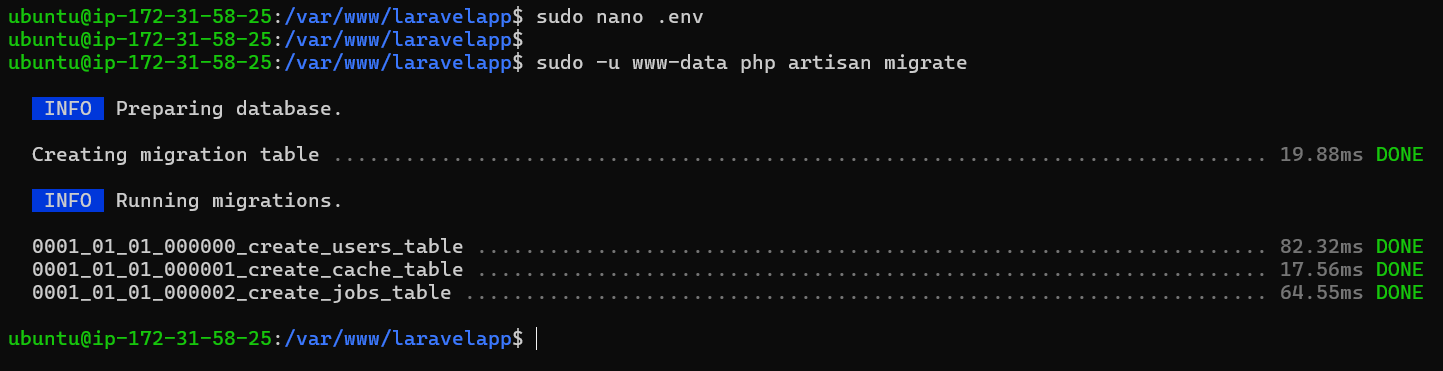
Finally, run the command below to migrate the database for your Laravel project.
sudo -u www-data php artisan migrate
Output of the Laravel database migration:
Setting up a virtual host for Laravel
In this section, you'll configure the virtual host file for Laravel. Make sure you have a local domain name ready for your Laravel development.
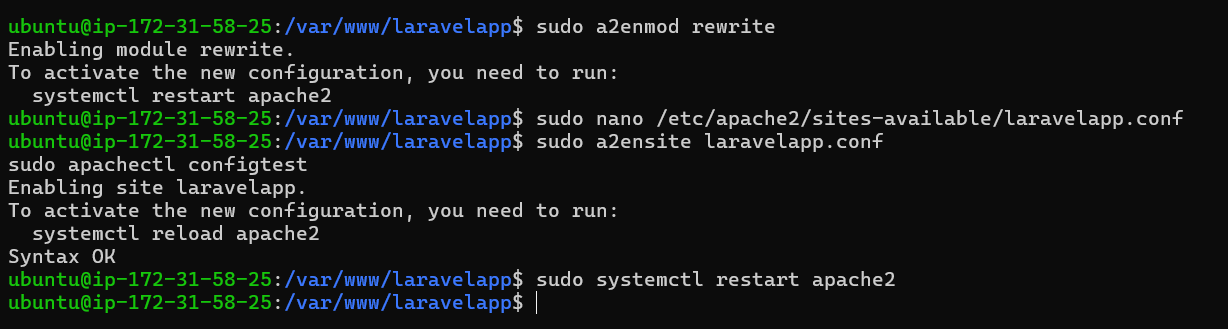
Before setting up the virtual host, enable the Apache rewrite module using the command below.
sudo a2enmod rewrite
Create a new virtual host configuration file at /etc/apache2/sites-available/laravelapp.conf using the nano editor.
sudo nano /etc/apache2/sites-available/laravelapp.conf
Add the following configuration and update the ServerName option with your Laravel domain name, such as laravelapp.local.
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerAdmin [email protected]
ServerName laravelapp.local
DocumentRoot /var/www/laravelapp/public
<Directory />
Options FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride None
</Directory>
<Directory /var/www/laravelapp>
AllowOverride All
</Directory>
ErrorLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/error.log
CustomLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/access.log combined
</VirtualHost>
Save the file and exit the editor.
Next, run the command below to enable the laravelapp.conf virtual host and check your Apache syntax. If there are no errors, you should see the message Syntax OK.
sudo a2ensite laravelapp.conf
sudo apachectl configtest
Restart the Apache service to apply the new Laravel virtual host configuration. Once Apache has restarted, your Laravel installation will be ready.
sudo systemctl restart apache2
Accessing Laravel Project
At this stage, you're ready to access your Laravel installation through the 'hosts' file. For Linux or macOS users, edit the /etc/hosts file with root privileges.
For Windows users, open the C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts file with administrator rights.
Add your Ubuntu server's IP address followed by the Laravel domain name as shown below:
192.168.5.30 laravelapp.local
Save and exit the file.
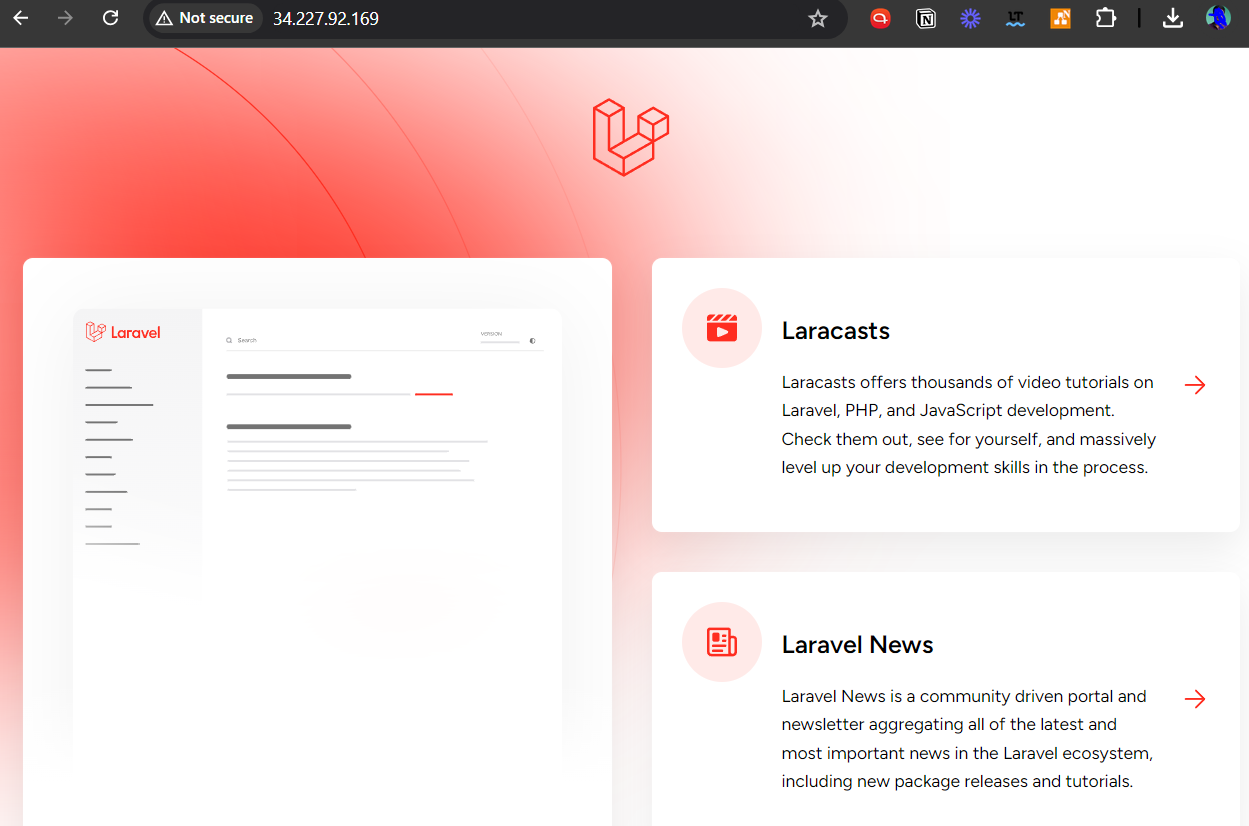
Now, navigate to http://laravelapp.local/ in your web browser. If the Laravel installation was successful, you should see the following page:
FAQs to Install Laravel on Ubuntu 24.04
What are the system requirements for installing Laravel on Ubuntu 24.04?
Laravel requires PHP 8.2 or later, along with necessary PHP extensions such as OpenSSL, PDO, Mbstring, Tokenizer, and XML.
What is the default port for the Laravel development server?
The default port is 8000. You can access your application at http://127.0.0.1:8000.
What is the purpose of the .env file in Laravel?
The .env file is used to configure environment variables for your application, such as database connections and application settings.
What is the Laravel Artisan command?
Artisan is the command-line interface included with Laravel, providing commands for various tasks, including migrations and running the server.
What is Laravel Mix?
Laravel Mix is a wrapper around Webpack for compiling assets like CSS and JavaScript.
How do I check the Laravel application logs?
Logs are located in storage/logs/laravel.log.
How do I enable Laravel's debug mode?
Set APP_DEBUG=true in the .env file.
Conclusion
We hope this tutorial helped you understand how to install Laravel on Ubuntu 24.04.
If you have any queries, please leave a comment below, and we’ll be happy to respond to them for sure.