Choose a different version or distribution
Introduction
Before we begin talking about how to install Tomcat on Ubuntu 22.04, let's briefly understand – What is Tomcat?
Tomcat, also known as Apache Tomcat, is a widely used open-source web server and servlet container. It provides a platform for hosting Java-based web applications and is compatible with various operating systems. Tomcat efficiently handles HTTP requests and delivers web content to users.
Its lightweight nature and easy configuration make it popular among developers. With its robust features, Tomcat enables the deployment of dynamic and scalable websites. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced developer, Tomcat simplifies the process of running Java web applications effectively.
This tutorial will guide you through the process of installing Tomcat 9 on Ubuntu 22.04. We will also address a few FAQs on how to install Tomcat on Ubuntu 22.04.
Advantages of Tomcat
- Open-source: Tomcat is freely available, making it cost-effective for businesses.
- Java Support: It serves as a reliable platform for hosting Java-based web applications.
- Lightweight: Tomcat's small footprint ensures efficient resource utilization and improved performance.
- Easy Configuration: Its user-friendly interface simplifies setup and deployment of web applications.
- Scalability: Tomcat allows for easy scaling and handling of increasing traffic demands on websites.
Prerequisites to Install Tomcat 9 on Ubuntu 22.04
- A non-root user with
sudoprivileges. - An Ubuntu 22.04 server.
Step 1 – Install JAVA
1) First, install OpenJDK 11. It is an implementation of the Java Platform. To update the packages index and install the OpenJDK 11 JDK package, run the following commands:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install openjdk-11-jdk
2) After installation, verify it by checking the version of JAVA.
java -version
3) You'll get an output like this:
Output
openjdk version "11.0.7" 2020-04-14
OpenJDK Runtime Environment (build 11.0.7+10-post-Ubuntu-3ubuntu1)
OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM (build 11.0.7+10-post-Ubuntu-3ubuntu1, mixed mode, sharing)
Step 2 – Create Tomcat User and Group
1) Create a new system user and group with a home directory of /opt/tomcat to run the Tomcat service. Enter the following command:
sudo useradd -m -U -d /opt/tomcat -s /bin/false tomcat
Step 3 – Download Tomcat
1) Check the Tomcat download page to see if a newer version is available.
2) After that, use wget to download the Tomcat zip file to the /tmp directory:
VERSION=9.0.71
wget https://downloads.apache.org/tomcat/tomcat-9/v${VERSION}/bin/apache-tomcat-${VERSION}.tar.gz
3) After downloading, extract the tar file to /opt/tomcat directory.
sudo tar -xf /tmp/apache-tomcat-${VERSION}.tar.gz -C /opt/tomcat/
4) Tomcat is typically updated regularly for security and to introduce new features. For more control, create a symbolic link called “latest” that points to the Tomcat installation directory.
sudo ln -s /opt/tomcat/apache-tomcat-${VERSION} /opt/tomcat/latest
5) Unpack the latest version, then update the symlink to point to it. Additionally, change the directory ownership to the user and group tomcat using:
sudo chown -R tomcat: /opt/tomcat
6) After that, the shell scripts in Tomcat's bin directory need to be made executable.
sudo sh -c 'chmod +x /opt/tomcat/latest/bin/*.sh'
These scripts are useful for starting, stopping, and managing Tomcat instances.
Step 4 – Create the SystemD Unit File
1) Open the text editor and create a tomcat.service unit file in the /etc/systemd/system/ directory.
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/tomcat.service
2) After that, paste the following configuration in /etc/systemd/system/tomcat.service:
/etc/systemd/system/tomcat.service
[Unit]
Description=Tomcat 9 servlet container
After=network.target
[Service]
Type=forking
User=tomcat
Group=tomcat
Environment="JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64"
Environment="JAVA_OPTS=-Djava.security.egd=file:///dev/urandom -Djava.awt.headless=true"
Environment="CATALINA_BASE=/opt/tomcat/latest"
Environment="CATALINA_HOME=/opt/tomcat/latest"
Environment="CATALINA_PID=/opt/tomcat/latest/temp/tomcat.pid"
Environment="CATALINA_OPTS=-Xms512M -Xmx1024M -server -XX:+UseParallelGC"
ExecStart=/opt/tomcat/latest/bin/startup.sh
ExecStop=/opt/tomcat/latest/bin/shutdown.sh
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
JAVA_HOME variable, if the path to Java installation is different.3) Then, save and close the file. Notify systemd that a new file exists.
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
4) Once done, enable the Tomcat service and start it.
sudo systemctl enable --now tomcat
5) You will need to check the service status.
sudo systemctl status tomcat
6) The result indicates that the Tomcat server is enabled and operational.
Output
tomcat.service - Tomcat 9 servlet container
Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/tomcat.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Tue 2020-05-12 17:58:37 UTC; 4s ago
Process: 5342 ExecStart=/opt/tomcat/latest/bin/startup.sh (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 5362 (java)
7) Now you can start, stop, even restart Tomcat as any other systemd service. Use the following command:
sudo systemctl start tomcat
sudo systemctl stop tomcat
sudo systemctl restart tomcat
Step 5 – Configure the Firewall
If you wish to access Tomcat from outside the local network, you must open port 8080. To do so, use the following command:
sudo ufw allow 8080/tcp
Step 6 – Configure the Tomcat Web Management Interface
To gain access to the Web Management Interface, you must create a user.
1) Navigate to the tomcat-users.xml file, as this is where Tomcat users and roles are defined.
2) Create a user with both admin-gui and manager-gui roles. This will enable access to the /host-manager/html URL and allow for the creation, deletion, and management of virtual hosts. The manager-gui will also let you deploy and undeploy web-applications without needing to restart the entire container through the /host-manager/html interface.
3) Open the tomcat-users.xml file. Create a new user with the following command:
sudo nano /opt/tomcat/latest/conf/tomcat-users.xml
<tomcat-users>
<!--Comments-->
<role rolename="admin-gui"/>
<role rolename="manager-gui"/>
<user username="admin" password="admin_password" roles="admin-gui,manager-gui"/>
</tomcat-users>
4) To increase security, change your username and password.
5) To access the web interface from a remote IP, remove the restrictions. However, this is not recommended for production systems, as it may have security implications.
You must enable access to the web interface from any location. To do this, open the following two files and comment out or remove the following lines:
For Manager app:
sudo nano /opt/tomcat/latest/webapps/manager/META-INF/context.xml
For Host Manager app:
sudo nano /opt/tomcat/latest/webapps/host-manager/META-INF/context.xml
<ContextantiResourceLocking="false" privileged="true" >
. . .
<!--
<Valve className="org.apache.catalina.valves.RemoteAddrValve"
allow="127\.\d+\.\d+\.\d+|::1|0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1" />
-->
. . .
</Context>
If you want to restrict access to the web interface to a specific IP, add the address to the list.
Use | to separate the IP addresses in the list. You can add a single IP address or can also use a regular expression.
After that, restart the Tomcat service to apply the changes.
Step 7 – Testing the Tomcat Installation
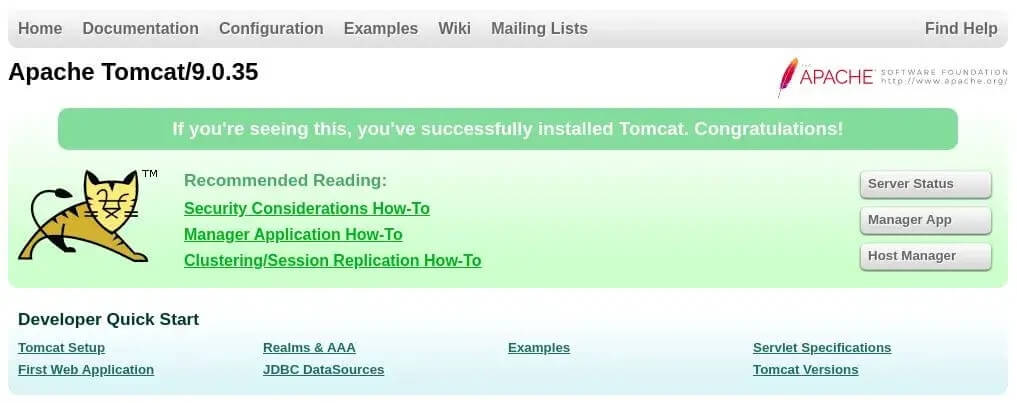
1) Proceed to open the browser, then type http://<your_domain_or_IP_address>:8080. Change your_domain_or_IP_address.
The screen will look like this:
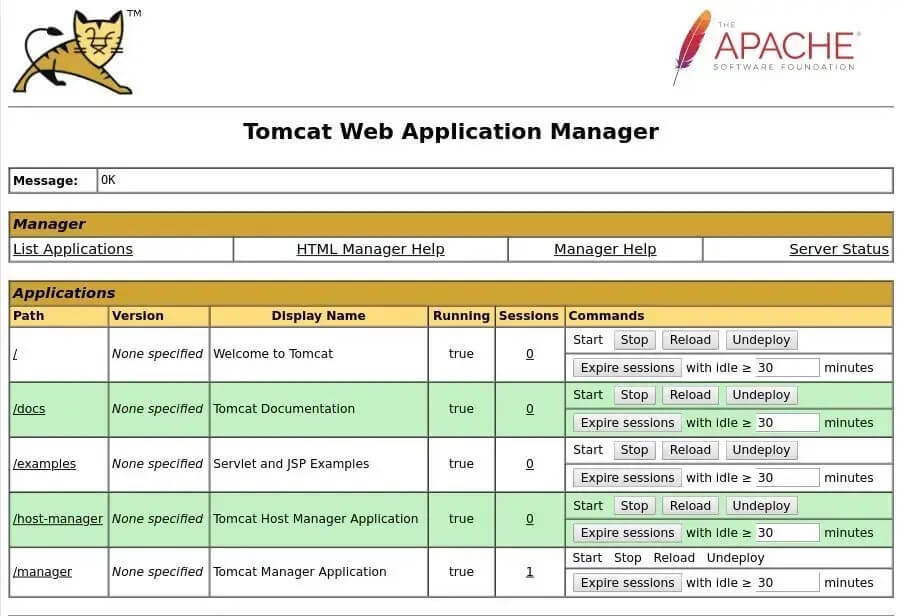
2) The Tomcat web application manager will be accessible at:
http://<your_domain_or_IP_address>:8080/manager/html
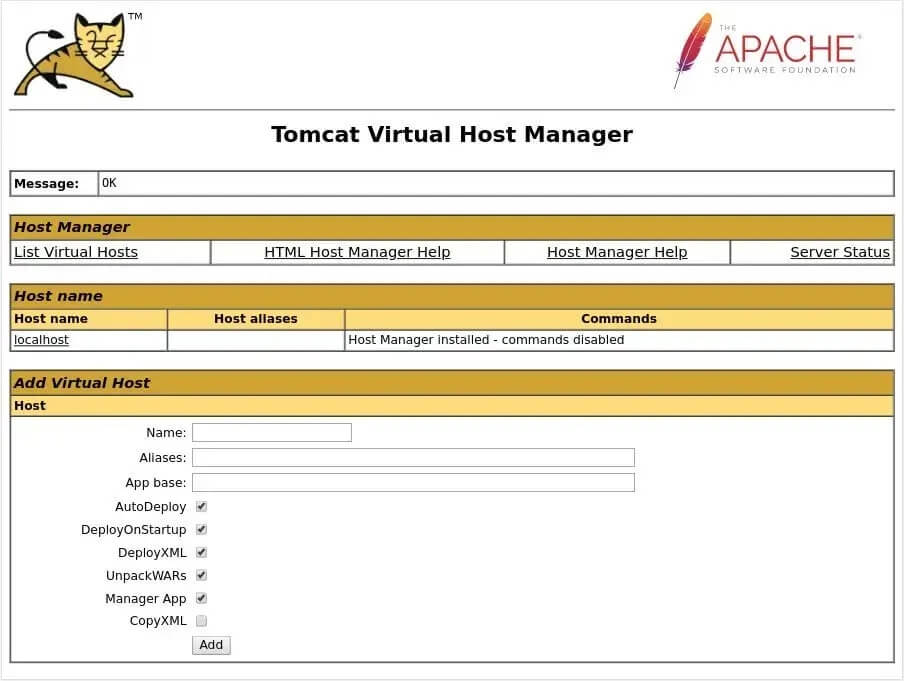
3) Moreover, the Tomcat Virtual Host Manager can be accessed at:
http://<your_domain_or_IP_address>:8080/host-manager/html
FAQs to Install Tomcat 9 on Ubuntu 22.04
Where should I install Tomcat 9 on Ubuntu?
Tomcat can be installed in any directory on Ubuntu. It is commonly installed in the /opt directory.
How can I start and stop Tomcat 9 on Ubuntu?
To start Tomcat, navigate to the Tomcat installation directory and run ./bin/startup.sh. To stop Tomcat, run ./bin/shutdown.sh.
How can I access the Tomcat Manager web interface?
After installing Tomcat, access the Manager web interface using the URL "http://localhost:8080/manager/html". Provide the necessary credentials to log in.
How can I deploy a web application in Tomcat 9?
Copy your web application's WAR file to the webapps directory in the Tomcat installation folder. Tomcat will automatically deploy the application.
Can I configure multiple instances of Tomcat on Ubuntu?
Yes, you can create multiple instances of Tomcat by duplicating the Tomcat installation directory and configuring them individually.
How can I auto-start Tomcat on Ubuntu startup?
Create a systemd service file for Tomcat and enable it using the systemctl command. This will ensure Tomcat starts automatically on system boot.
Conclusion
We hope this detailed tutorial helped you understand how to install Tomcat 9 on Ubuntu 20.04. To learn more about Tomcat installation on Ubuntu 20.04, check out the official Tomcat installation document.
If you have any queries, please leave a comment below, and we’ll be happy to respond to them for sure.