Introduction
In this tutorial, you will see how to list and filter installed packages on Debian. We will also demonstrate how to count installed packages and determine a package's version. It also determines whether a given package is installed or not.
Knowing how to list installed packages can be useful when you need to install the same packages on a different machine. It's also helpful when you wish to reinstall your Debian-based system.
List Installed Packages with Apt
The package management system's command-line interface Apt combines the most useful features of apt-get and apt-cache.
Run the following command to list all packages that are currently installed on your system:
sudo apt list --installed
Output
adduser/stable,now 3.115 all [installed]
apt/stable,now 1.4.8 amd64 [installed]
apt-listchanges/stable,now 3.10 all [installed]
apt-utils/stable,now 1.4.8 amd64 [installed]
autoconf/stable,now 2.69-10 all [installed]
automake/stable,now 1:1.15-6 all [installed]
autotools-dev/stable,now 20161112.1 all [installed,automatic]
base-files/stable,now 9.9+deb9u5 amd64 [installed]
base-passwd/stable,now 3.5.43 amd64 [installed]
bash/stable,now 4.4-5 amd64 [installed]
A list of all installed packages, along with details on their versions and architecture, will be shown by the command. The output's right-most column indicates if the package was installed automatically as a dependency of another package.
It is a good idea to pipe the output to the less command to make it simpler to read because the packages list is lengthy:
sudo apt list --installed | less
Use the grep command to filter the results and see if a particular package is installed. As an illustration, you might type the following to check if the tmux package is installed on the system:
sudo apt list --installed | grep tmux
Output
tmux/stable,now 2.3-4 amd64 [installed]
As you can see in the output, you have tmux 2.3-4 installed on your system.
List Installed Packages with dpkg-query
The command line tool dpkg-query can be used to view details about packages listed in the dpkg database.
Type the following to receive a list of all installed packages:
sudo dpkg-query -l | less
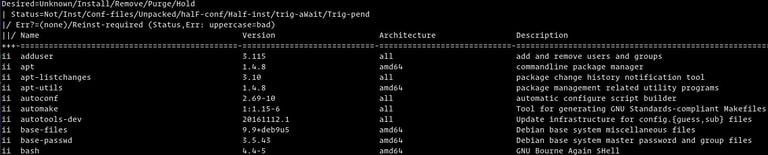
A list of all installed packages, together with their versions, architecture, and a brief description, will be shown by the command.
The grep command can be used to filter the output of dpkg-query -l:
sudo dpkg-query -l | grep package_name_to_search
Create a List of all Installed Packages
When you run the following command, a file called packages_list.txt will be created on your Debian system with a list of all installed packages:
sudo dpkg-query -f '${binary:Package}\n' -W > packages_list.txt
With the list in hand, you can use the following methods to install the same packages on your new server:
sudo xargs -a packages_list.txt apt install
Count the Number of Installed Packages
You can use the same command for creating a packages list to determine how many packages are installed on your system. Instead of sending the output to a file, pipe it to the wc command to count the lines:
sudo dpkg-query -f '${binary:Package}\n' -W | wc -l
The number of installed packages will be shown in the output:
Output
466
Conclusion
You now understand how to list and filter installed packages on your Debian system.
If you have any queries, please leave a comment below and we’ll be happy to respond to them.

