Introduction
In today’s digital age, businesses face a critical challenge: choosing the right cloud infrastructure provider to ensure seamless operations and robust security. With numerous options available, the decision can be overwhelming, leading to potential inefficiencies and increased costs.
However, understanding the key players and their unique offerings can simplify this choice. This guide will help you navigate the complexities of cloud infrastructure, ensuring you select the best provider for your needs.
Criteria for Evaluating Cloud Infrastructure Providers
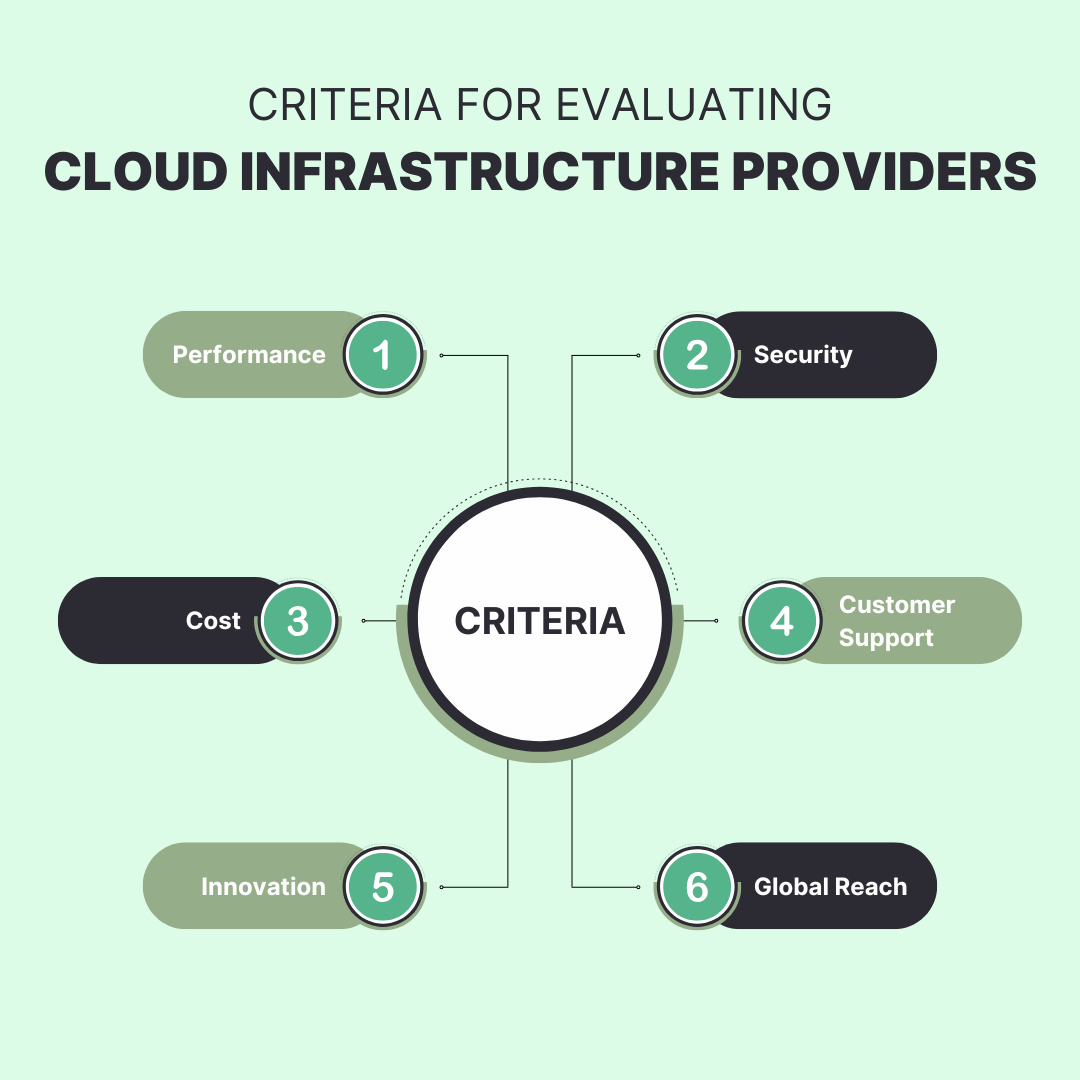
When selecting a cloud infrastructure provider, it’s crucial to evaluate several key factors to ensure you make an informed decision that aligns with your business needs. Following are the criterias to consider:
Performance: Assess the provider's ability to deliver consistent speed and reliability. Look for metrics on uptime guarantees, latency, and scalability. Ensure their infrastructure can handle your workload demands and provide smooth performance under peak conditions.
Security: Security is paramount in cloud computing. Examine the provider’s compliance with industry standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, or ISO 27001. Review their data encryption methods, intrusion detection systems, and overall threat management strategies. A robust security framework will protect your data from breaches and cyber threats.
Cost: Understand the pricing model and assess whether it aligns with your budget. Providers generally offer three types of pricing options: pay-as-you-go, reserved instances, and subscription-based pricing. Be aware of any additional costs such as data transfer fees, storage, or support services. Evaluate the cost-effectiveness and potential hidden charges to avoid unexpected expenses.
Customer Support: Dependable customer support can greatly impact the speed at which issues are resolved. Check the availability of support channels—such as 24/7 live chat, phone support, or email. Review customer service reviews and ensure the provider offers comprehensive resources and documentation.
Innovation: The cloud landscape is continually evolving. Look for providers that offer the latest technologies and services, such as advanced analytics, AI integration, or serverless computing. Staying ahead with cutting-edge features can provide a competitive advantage and support future growth.
Global Reach: Consider the provider's network of data centers and their geographic coverage. A broad global presence ensures low latency and high availability for users in different regions. It also supports disaster recovery and redundancy needs.
Detailed Profiles of Top Cloud Infrastructure Providers
The cloud infrastructure market is dominated by a few key players, each offering a unique set of services and strengths. Understanding these providers' offerings will help you determine which one best fits your needs. Here’s a detailed overview of the leading contenders:
Amazon Web Services (AWS): AWS is the market leader, known for its extensive service portfolio and global reach. It offers a broad range of tools, including compute power, storage options, and advanced technologies like AI and machine learning.
AWS is perfect for businesses that require scalable solutions and a diverse range of services. However, its pricing can be complex, and costs can quickly add up if not managed carefully.
Microsoft Azure: Azure is a strong competitor, particularly favored by enterprises already invested in Microsoft products. It integrates seamlessly with existing Microsoft solutions like Office 365 and Windows Server, making it a natural choice for businesses in that ecosystem.
Azure also excels in hybrid cloud environments, offering robust support for integrating on-premises and cloud resources. Its pricing is competitive, especially for existing Microsoft customers.
Google Cloud Platform (GCP): GCP is well-known for its innovative approach, especially in the fields of data analytics and machine learning. It offers industry-leading tools like BigQuery and TensorFlow, making it a top choice for companies focused on data-driven projects.
GCP’s infrastructure is designed for high performance, with a global network that supports low-latency applications. While it’s not as extensive as AWS or Azure in service offerings, GCP’s pricing is transparent and often more affordable for specific use cases.
IBM Cloud: IBM Cloud specializes in hybrid cloud solutions and is known for its strong emphasis on security and compliance. It’s a preferred choice for industries with stringent regulatory requirements, such as healthcare and finance.
IBM’s AI capabilities, powered by Watson, also offer advanced analytics and cognitive services. However, IBM Cloud may not be as broad in its service offerings as AWS or Azure, making it more suitable for niche applications.
Oracle Cloud: Oracle Cloud is designed specifically for enterprises that require high-performance computing and effective database management. It’s particularly strong in offering solutions for running Oracle software, such as Oracle Database and Oracle Applications, with optimal efficiency.
Oracle Cloud also provides robust support for hybrid deployments and is competitively priced for Oracle-centric workloads. However, it might not be the best fit for businesses looking for a wide array of non-Oracle services.
Comparative Analysis of Top Cloud Infrastructure Providers
Selecting the right cloud infrastructure provider requires a thorough comparison across several critical dimensions. Here’s a breakdown of how the leading providers—AWS, Azure, GCP, IBM Cloud, and Oracle Cloud—stack up against each other:
1. Performance: AWS, Azure, and GCP are industry leaders in terms of performance, offering robust global networks with low latency and high availability. AWS boasts the largest number of data centers globally, providing excellent redundancy and disaster recovery options.
Azure follows closely, particularly excelling in hybrid cloud scenarios. GCP is known for its high-performance computing capabilities, especially for data-intensive workloads. IBM Cloud and Oracle Cloud, while strong in specific areas, tend to be more niche, with IBM focusing on hybrid and enterprise solutions and Oracle on high-performance databases.
2. Security: All providers offer comprehensive security features, including encryption, identity management, and compliance with major industry standards. AWS and Azure provide the most extensive range of compliance certifications, making them suitable for highly regulated industries.
GCP emphasizes data security, leveraging its expertise in big data. IBM Cloud stands out for its focus on enterprise-grade security and compliance, making it a preferred choice for industries like healthcare and finance. Oracle Cloud also offers robust security, particularly for Oracle-centric environments, ensuring that sensitive data is well-protected.
3. Cost: Cost comparison varies based on specific use cases. AWS offers a wide range of pricing options, but managing costs can be complex due to its vast service catalog. Azure’s pricing is competitive, especially for businesses already using Microsoft products, with discounts available for existing customers.
GCP is often praised for its transparent pricing, particularly in areas like data analytics. IBM Cloud and Oracle Cloud are typically more cost-effective for specialized workloads, such as enterprise and database management, but might not be the cheapest options for more general use cases.
4. Feature Set: AWS leads in the breadth and depth of its service offerings, with over 200 services ranging from basic compute and storage to advanced machine learning and IoT. Azure is a close second, particularly strong in integrations with Microsoft software and hybrid cloud.
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) excels in big data and machine learning, providing powerful tools such as BigQuery and TensorFlow. IBM Cloud’s strength lies in its AI-powered solutions and hybrid cloud capabilities, while Oracle Cloud is unmatched in database management, offering high-performance computing tailored to Oracle environments.
5. Global Reach: AWS has the most extensive global presence, with data centers in more regions than any other provider. Azure’s global network is also vast, particularly in regions where Microsoft has a strong enterprise presence.
GCP, while slightly more limited in geographic coverage, still offers a robust global network with low-latency connections. IBM Cloud and Oracle Cloud have more region-specific data centers, making them ideal for businesses with specific geographic requirements but potentially limiting for global operations.
Industry Trends and Future Outlook
The cloud infrastructure landscape is rapidly evolving, driven by new technologies and changing business requirements. Staying ahead of these trends is essential for businesses looking to maximize the benefits of cloud computing. Following are the key industry trends shaping the future of cloud infrastructure:
- Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Strategies: Businesses are increasingly adopting hybrid and multi-cloud approaches to avoid vendor lock-in, enhance flexibility, and optimize costs. Hybrid cloud allows companies to combine on-premises infrastructure with cloud services, enabling a seamless integration of legacy systems and new cloud technologies. Multi-cloud strategies, on the other hand, involve using multiple cloud providers to leverage the best features of each and distribute risk.
- Edge Computing: As data generation continues to grow exponentially, edge computing is becoming more critical. By processing data closer to its source, edge computing reduces latency and bandwidth usage, making it ideal for applications requiring real-time processing, such as IoT devices and autonomous vehicles. Cloud providers are increasingly investing in edge computing solutions to meet the demand for faster, more efficient data processing.
- AI and Machine Learning Integration: AI and machine learning are becoming integral components of cloud services. Providers like AWS, Azure, and GCP are expanding their offerings in this area, providing tools that enable businesses to build and deploy AI models at scale. This trend is expected to continue, with more advanced AI capabilities being integrated into cloud platforms, allowing businesses to automate processes, gain deeper insights from data, and innovate faster.
- Sustainability and Green Cloud: With growing awareness of environmental impact, sustainability is becoming a key focus for cloud providers. Companies are increasingly looking for providers that offer green cloud solutions, which use energy-efficient data centers powered by renewable energy. Providers are responding by committing to carbon neutrality and developing services that help customers reduce their carbon footprint. This trend is likely to intensify as businesses and consumers prioritize sustainability in their operations.
- Security Enhancements: As cyber threats become more sophisticated, security remains a top priority in cloud infrastructure. Providers are continuously improving their security offerings, incorporating advanced threat detection, encryption, and identity management features. The future will likely see even more robust security frameworks, with a focus on AI-driven threat intelligence and zero-trust security models.
- Serverless Computing: Serverless computing is becoming increasingly popular, as it enables developers to build and run applications without having to manage the underlying infrastructure. This model simplifies operations, reduces costs, and allows for greater scalability. As serverless technology matures, it is expected to become a standard offering across cloud platforms, further streamlining application development and deployment.
Choosing the Right Cloud Infrastructure Provider
Selecting the optimal cloud infrastructure provider is vital for your business’s performance, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. Keep the following factors in mind for a head start in making an informed choice:
- Assess Your Business Needs: Begin by assessing your specific needs. Consider the type of applications you run, your data storage needs, and any compliance regulations your industry must adhere to. For example, if you need advanced AI capabilities or big data processing, Google Cloud Platform (GCP) might be the best fit. If your business heavily relies on Microsoft products, the seamless integration offered by Azure could be beneficial.
- Evaluate Performance and Reliability: Seek providers known for high uptime, low latency, and global accessibility. AWS, Azure, and GCP offer robust infrastructure with extensive data center networks, ensuring your applications run smoothly with minimal downtime. For mission-critical applications, consider providers with strong service-level agreements (SLAs) and disaster recovery options.
- Consider Security and Compliance: Security is paramount, especially if your business handles sensitive data. Ensure the provider offers comprehensive security features such as data encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular security updates. Additionally, check if they comply with relevant industry standards like GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS. IBM Cloud, for instance, is known for its focus on security and compliance, making it a strong choice for regulated industries.
- Analyze Cost Structure: Different service providers offer a range of pricing models, including pay-as-you-go, reserved instances, and subscription plans. Consider your budget and analyze the total cost of ownership, including hidden fees like data transfer or storage costs. AWS provides a wide range of pricing options but can be complex to navigate, while GCP is often praised for its transparent and competitive pricing.
- Assess Support and Customer Service: Reliable customer support can be crucial, especially during migration or when troubleshooting issues. Look for providers that offer 24/7 support with multiple channels, including live chat, phone, and email. Additionally, explore the availability of detailed documentation, tutorials, and community forums. Azure and AWS are known for their extensive support resources, while smaller providers may offer more personalized service.
- Future-Proofing and Innovation: Consider the provider’s commitment to innovation and future-proofing. Providers that regularly introduce new services, like serverless computing, AI integration, and edge computing, can help your business stay ahead of the curve. AWS and GCP, for example, are leaders in introducing cutting-edge technologies that can give your business a competitive advantage.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Real-world examples of businesses successfully leveraging cloud infrastructure can provide valuable insights and inspiration for your own cloud journey. Here are a few notable case studies that highlight how different companies have utilized cloud providers to achieve their goals:
1. Netflix (AWS): Netflix is a leading example of a company succeeding in the cloud. By moving its entire video streaming platform to Amazon Web Services (AWS), Netflix has achieved unmatched scalability and reliability. AWS’s global infrastructure enables Netflix to deliver content seamlessly to millions of users worldwide, even during peak demand periods.
The move to AWS has also allowed Netflix to innovate rapidly, using advanced analytics and machine learning to improve user recommendations and optimize streaming quality.
2. Adobe (Microsoft Azure): Adobe leveraged Microsoft Azure to transition its popular Creative Cloud suite from traditional software to a cloud-based subscription model. This shift enabled Adobe to offer continuous updates, enhanced collaboration tools, and better customer support.
Azure’s robust security features and seamless integration with Adobe’s existing systems made it the ideal platform for this transformation. As a result, Adobe has been able to scale its services globally, delivering a consistent and secure experience to millions of creative professionals.
3. Spotify (Google Cloud Platform): Spotify leveraged Google Cloud Platform (GCP) to strengthen its data analytics capabilities. With GCP’s BigQuery and data processing tools, Spotify has been able to analyze vast amounts of user data in real-time, enabling personalized music recommendations and targeted advertising.
This data-driven approach has helped Spotify retain and grow its user base, while GCP’s scalable infrastructure supports the platform’s rapid expansion into new markets.
4. American Airlines (IBM Cloud): American Airlines utilized IBM Cloud to enhance its IT infrastructure and customer experience. By adopting a hybrid cloud approach, the airline integrated its legacy systems with IBM Cloud, enhancing operational efficiency and agility.
This transition allowed American Airlines to offer new services, such as personalized customer interactions and more efficient baggage tracking. IBM’s focus on security and compliance was crucial for the airline, ensuring that sensitive customer data was protected throughout the process.
5. Zoom (Oracle Cloud): As demand for remote communication tools skyrocketed during the COVID-19 pandemic, Zoom needed to scale its operations rapidly. Oracle Cloud provided the necessary infrastructure to handle the surge in users, offering low-latency performance and reliable connectivity.
The partnership with Oracle Cloud allowed Zoom to maintain its service quality during unprecedented growth, reinforcing its position as a leading video conferencing platform.
Key Takeaways
- Evaluate key criteria like performance, security, cost, and customer support when selecting a cloud infrastructure provider.
- Understand the unique strengths of top providers—AWS, Azure, GCP, IBM Cloud, and Oracle Cloud—and match them to your business needs.
- Stay ahead by adopting industry trends such as hybrid/multi-cloud strategies, edge computing, AI integration, and sustainability efforts.
- Learn from case studies to see how businesses have successfully leveraged cloud infrastructure for innovation and growth.
- Make informed decisions by aligning your choice with both current needs and long-term goals to maximize the benefits of cloud infrastructure.
Conclusion
Choosing the appropriate cloud infrastructure provider is a crucial decision that can greatly affect your business’s efficiency, scalability, and capacity for innovation. This guide has explored the top providers—AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, IBM Cloud, and Oracle Cloud—highlighting their strengths and key considerations for evaluation. We've also discussed the importance of aligning your choice with your specific needs, whether it's performance, security, cost, or future growth.
In an era of rapid technological advancement, staying informed about industry trends and carefully assessing your options ensures you make a decision that not only meets your current needs but also supports your long-term goals. By choosing wisely, you can leverage cloud infrastructure to drive innovation, enhance customer experiences, and achieve sustainable success.

